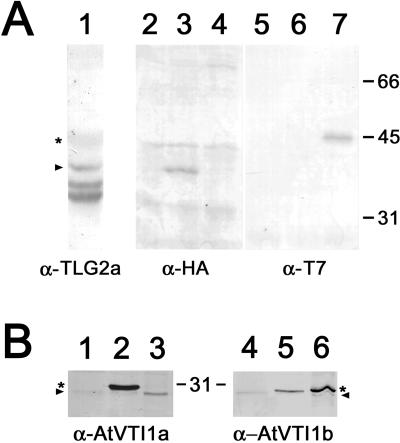
Figure 4.
Characterization of antibodies and epitope tags for AtTLG2a/b and AtVTI1a/b. (A) A microsomal extract of wild-type Arabidopsis (lane 1) was probed with affinity-purified antiserum to AtTLG2a. Full-length AtTLG2a is indicated by the arrowhead, and the smaller bands represent proteolytic breakdown products (see text). Antiserum to AtTLG2a cross-reacts weakly with AtTLG2b, which is indicated by the asterisk. Total protein extracts from either wild type (lanes 2 and 5) or plants expressing either HA-AtTLG2a (lanes 3 and 6) or T7-AtTLG2b (lanes 4 and 7) were probed with antisera specific to the epitope tags. Lanes 2–4 were probed with rabbit anti-HA to indicate HA-AtTLG2a, whereas lanes 5–7 were probed with mouse T7 mAbs to indicate T7-AtTLG2b. (B) Total extracts of wild-type Arabidopsis (lanes 1 and 4), plants expressing T7-AtVTI1a (lanes 2 and 5), or plants expressing HA-AtVTI1b (lanes 3 and 6) were probed with rabbit polyclonal antisera raised to either AtVTI1a (lanes 1–3) or AtVTI1b (lanes 4–6). In each case, the endogenous AtVTI1a or AtVTI1b is indicated by the arrowhead, and the epitope-tagged protein is indicated by the asterisk.