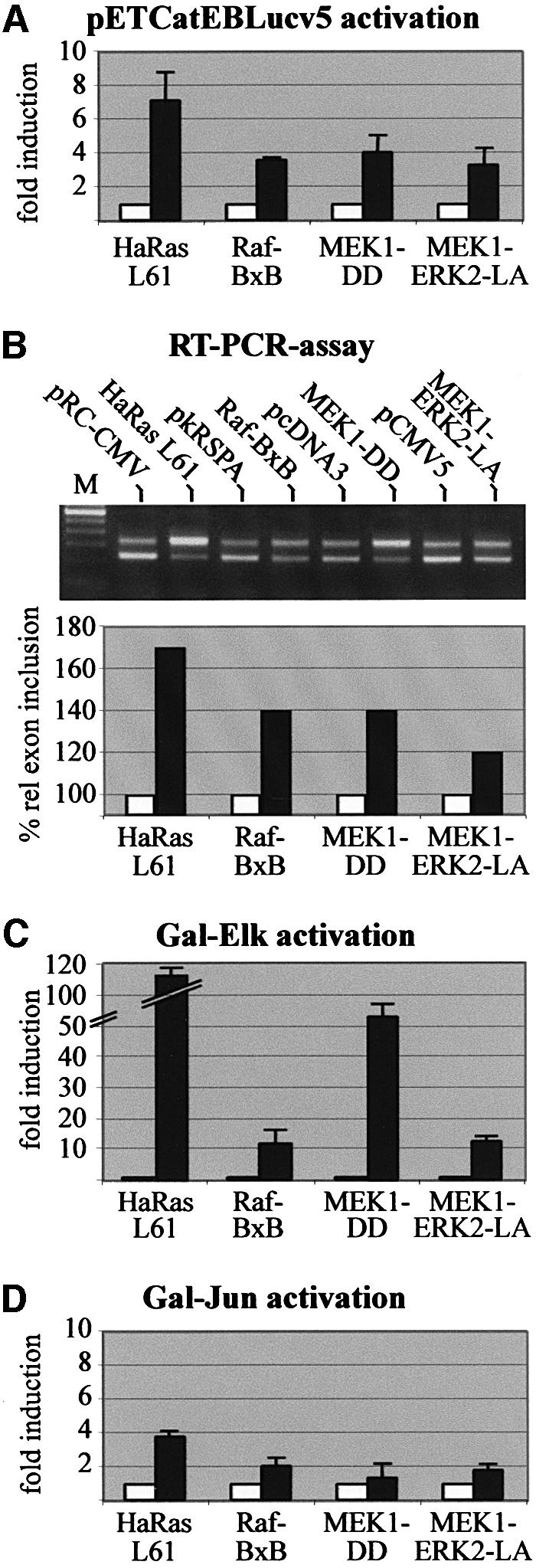
Fig. 4. Inclusion of CD44 exon v5 is induced by activation of the ERK MAP-kinase pathway. (A) Detection of CD44 v5 exon inclusion by luciferase activity. LB-17 cells were co-transfected with 2 µg of the pETCatEBLucv5 splice reporter construct and 2 µg of an expression vector for constitutively active HaRas L61, Raf-BxB, MEK1-DD or MEK1-ERK2-LA (filled bars) or the corresponding empty vectors (open bars). Each bar represents values of three independent experiments. Standard deviations are indicated on top of the bars. (B) Detection of CD44 v5 exon inclusion by RT–PCR analysis. LB-17 were co-transfected with 2 µg of pETv5 and 2 µg of constitutively active signaling mutants or vector controls as indicated (pRC-CMV, pkRSPA, pcDNA3, pCMV5). RT–PCR bands were quantified densitometrically after scanning using the Fuji Aida programme. For calculating percentage relative exon inclusion the value of % exon inclusion of control vectors was set to 100%. (C and D) To test for activation of the ERK and JNK pathways, LB-17 cells were co-transfected with 0.2 µg of a construct expressing the Gal-Elk fusion protein or 0.8 µg of a Gal-Jun expression vector and 0.8 µg of the pG5.E4Δ38lux3 luciferase reporter plus 2 µg of control vectors (left bars, open) or expression constructs for the signaling mutants indicated (right bars, filled). Luciferase assays were performed 24 h after transfection.
