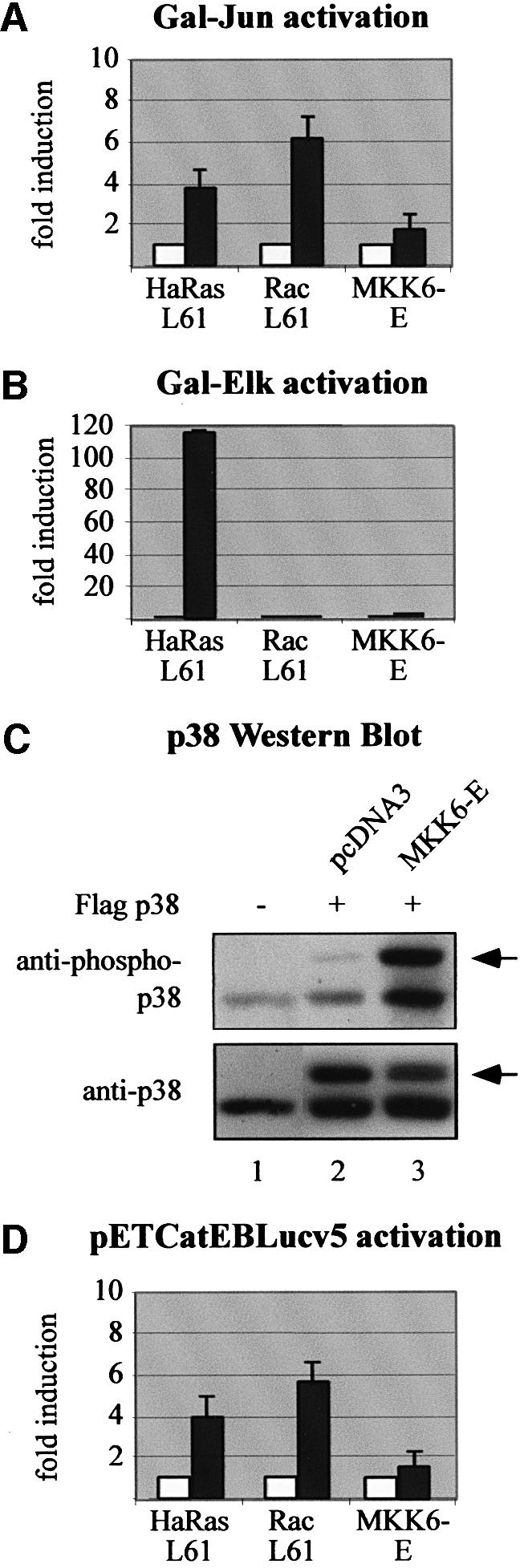
Fig. 6. Inclusion of CD44 exon v5 can be induced by constitutively active Rac. (A and B) JNK kinase pathway (A) and ERK pathway (B) activity was determined by co-transfection of LB-17 cells with the Gal-Jun or Gal-Elk luciferase reporter system and 2 µg of plasmids expressing constitutively active Ras (HaRas L61), Rac (Rac L61) or MKK6 (MKK6-E) (right bars, filled), or with a corresponding empty vector (left bars, open). (C) Activation of p38 MAP kinase after co-transfection of MKK6-E. LB-17 cells were co-transfected with 20 µg of a Flag-p38 expression construct (lanes 2 and 3) and 20 µg of a plasmid expressing constitutively active MKK6-E or pcDNA3 as control. Flag-tagged p38 (arrow) has a lower electrophoretic mobility compared with endogenous p38 (compare with sample where a control vector has been transfected instead of the Flag-p38 construct, lane 1). (D) Activation of CD44 v5 exon inclusion upon expression of constitutively activated Rac. Two micrograms of the luciferase splice reporter pETCatEBLucv5 were co-transfected with 2 µg of plasmids expressing HaRas L61, Rac L61 or MKK6-E (filled bars), or with an empty expression plasmid (open bars). Cells were harvested 24 h after transfection and luciferase activity was determined.
