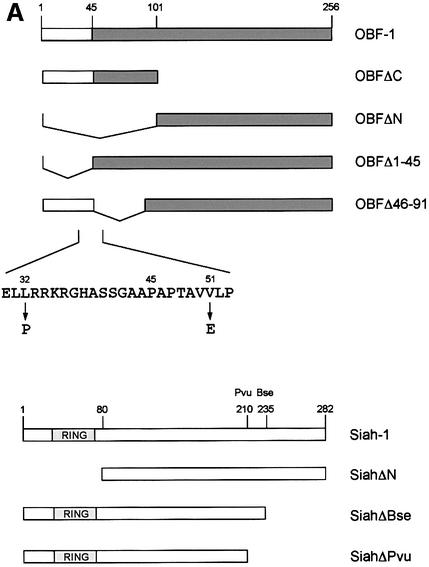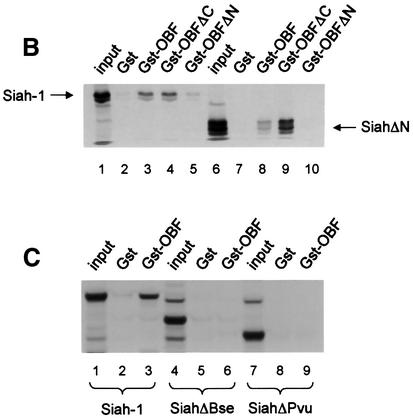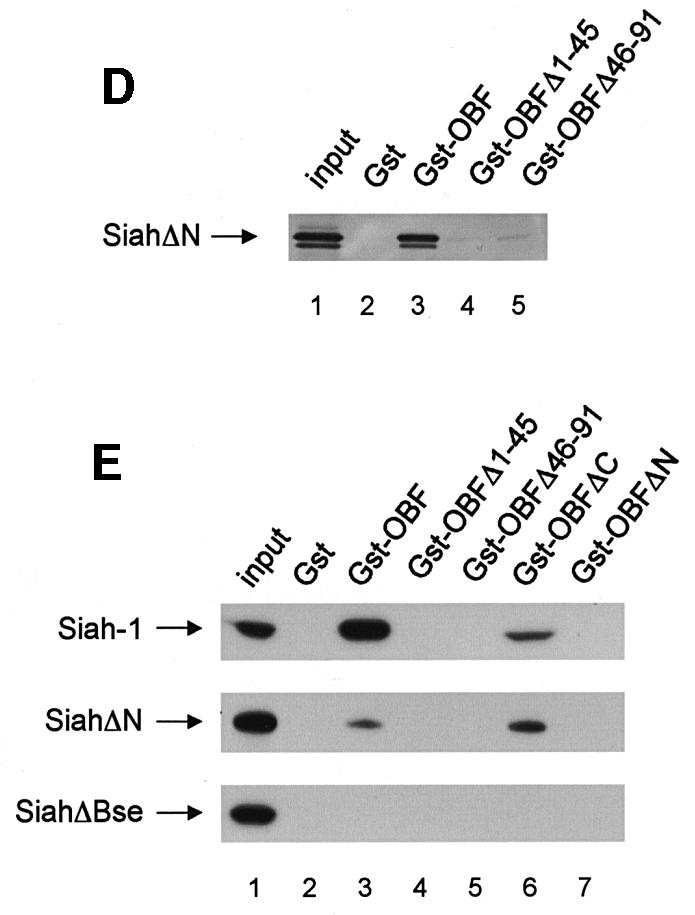
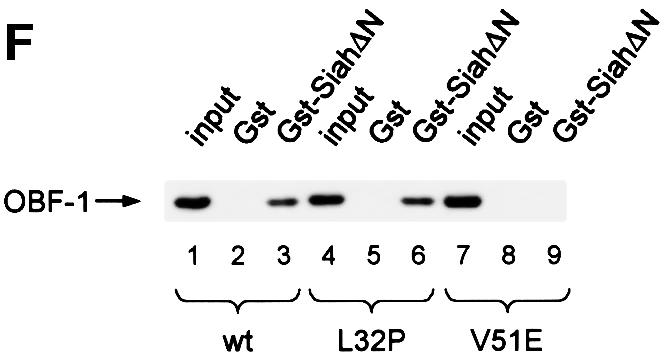
Fig. 2. OBF-1 and Siah-1 interact in vitro. (A) Schematic representation of the cDNAs used in this study. Depending on the experiment and as indicated in the relevant figure legends, the different proteins were expressed in bacteria as GST fusion proteins, made in reticulocyte lysate or expressed in eukaryotic cells from an appropriate expression vector. For OBF-1, the open rectangle represents the region that is necessary for interaction with the POU domain and DNA (Gstaiger et al., 1996; Chasman et al., 1999). (B–D) In vitro pull-down assays. Equal amounts of GST–OBF-1 fusion proteins as indicated were incubated with 35S-labeled Siah-1 proteins. After extensive washing, radioactive protein that was retained was visualized by SDS–PAGE followed by autoradiography. (E) Equal amounts of extracts from 293T cells transiently transfected with expression vectors for HA-tagged Siah-1, SiahΔN or SiahΔBse were incubated with beads loaded with GST–OBF-1 fusion proteins, as indicated. After extensive washing, bound proteins were run on SDS–PAGE and retained Siah was detected by western blotting using an anti-HA antibody. (F) Extracts from 293T cells transfected with Myc-tagged OBF-1 constructs as indicated were incubated with GST alone or GST–SiahΔN on glutathione beads. Subsequent analysis was carried out as in (E).