Figure 2.
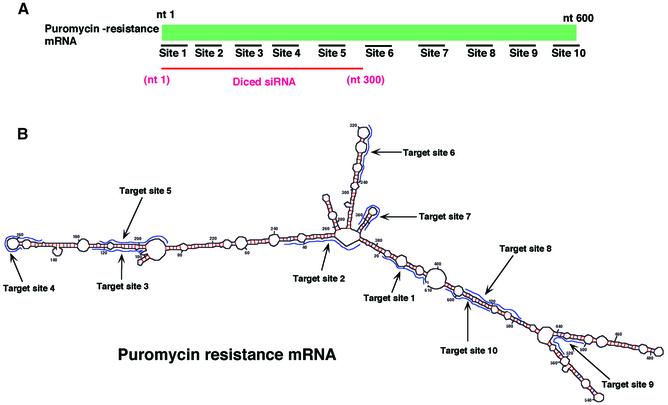
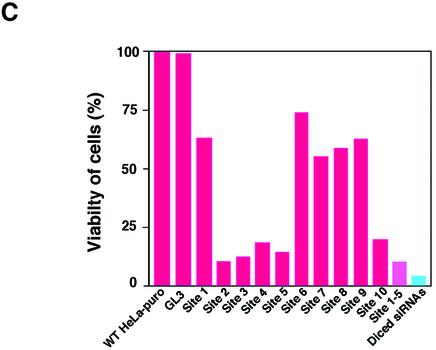
Suppression of the expression of an exogenous puromycin-resistance gene. (A) Ten sites (sites 1–10) were chosen as targets for synthetic siRNAs, as detailed in the text. For preparation of diced siRNAs, long dsRNAs corresponding to the 5′ region of the puromycin-resistance gene (nucleotides 1–300) were generated and treated with re-hDicer. (B) The secondary structure of the puromycin-resistance mRNA as predicted by the mfold program (24). (C) Diced siRNAs were the most effective suppressors of the expression of the exogenous puromycin-resistance gene (as indicated by the bar on the far right of the histogram). The efficiency of transfections with siRNAs was monitored with a reporter gene for luciferase from Renilla.