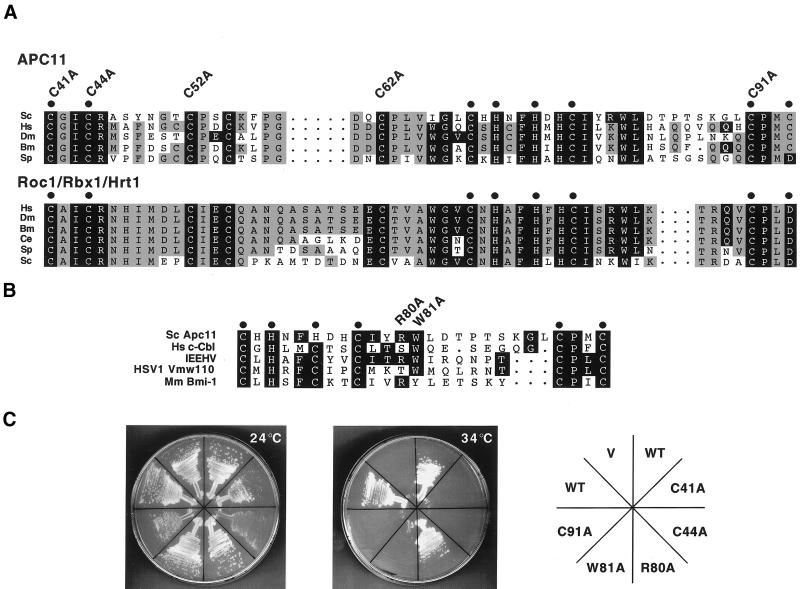
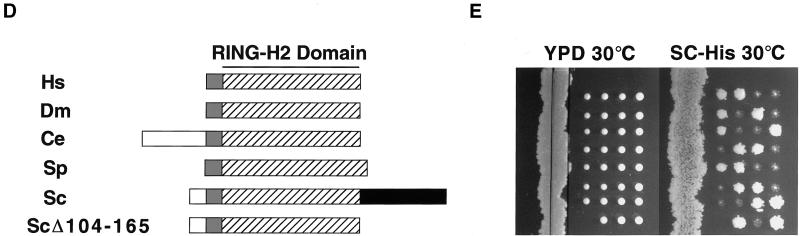
Figure 2.
Mutational analysis of the RING-H2 finger protein Apc11p. (A) Alignment of APC11 and Roc1/Rbx1/Hrt1 RING-H2 finger domains from various species, including Homo sapiens (Hs), Drosophila melanogaster (Dm), Bombyx mori (Bm), Caenorhabditis elegans (Ce), Schizosaccharomyces pombe (Sp), and Saccharomyces cerevisiae (Sc). Residues conserved between both protein families are shaded black, while those conserved only among APC11 or Roc1/Rbx1/Hrt1 family members are shaded gray. Cysteines and histidines predicted to mediate zinc binding are denoted by dots. Apc11p cysteine residues 41, 44, 52, 62, and 91 were individually mutated to alanine, and mutants were subsequently tested by complementation analysis, as described in C. (B) Alignment of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae Apc11p RING-H2 domain with RING domains from c-Cbl, the ENX fragment of the immediate early equine herpes virus protein (IEEHV), herpes simplex virus 1 protein Vmw110, and Bmi-1. Tryptophan 81 of Apc11p corresponds to c-Cbl tryptophan 408, which is essential for full E3 activity in vitro (Joazeiro et al., 1999). R80 and W81 were individually mutated to alanine, and the mutants tested for complementation of the apc11–13 ts allele. (C) Complementation analysis was performed by transforming the apc11–13 temperature sensitive strain (YAP201) with centromeric plasmids expressing either wild-type Apc11p (WT) or the mutant versions described in A and B (C41A, C44A, R80A, W81A, C91A). Empty vector (V) was employed as a negative control. Transformed cells were allowed to grow at the permissive temperature of 24°C before being restreaked to selective medium at either 24°C (left) or the restrictive temperature of 34°C (center). (D) Schematic depiction of APC11 proteins from various species. The RING-H2 domain is indicated by a hatched box. S. cerevisiae Apc11p contains a C-terminal extension (residues 104–165, shaded black) not found in other family members. (E) Diploid cells harboring one copy of a truncated version of APC11 (APC11Δ104–165) were sporulated, and the tetrads analyzed for viability on YPD (left panel). Spore colonies were then replica-plated to SC-His to confirm 2:2 segregation of wild-type APC11 (His−) and APC11Δ104–165 (His+) (right panel).