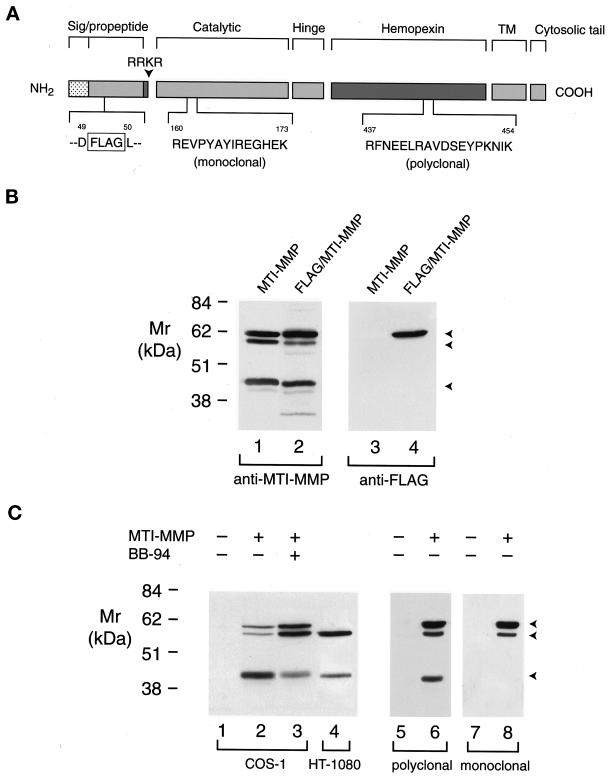
Figure 2.
Processing of proMT1-MMP in COS-1 and HT-1080 cells. (A) A scheme of MT1-MMP epitopes. Wild-type MT1-MMP and MT1-MMP containing a FLAG epitope inserted in the prodomain were detected with antibodies directed against a 14-amino acid residue (R160 to K173) in the catalytic domain, an 18-amino acid residue (R437 to K454) in the hemopexin domain, or a FLAG epitope inserted between residues D49 and L50 in the prodomain. (B) Western blot analysis of FLAG/MT1-MMP expression in COS-1 cells. COS-1 cells were transiently transfected with MT1-MMP or FLAG/MT1-MMP expression vectors. Triton X-114 extracts were then analyzed by immunoblotting with either hemopexin domain–specific polyclonal antisera (lanes 1 and 2) or anti-FLAG mAb (lanes 3 and 4). Although anti-MT1-MMP polyclonal antisera recognized both wild-type MT1-MMP (lane 1) and FLAG/MT1-MMP (lane 2), the anti-FLAG mAb recognized the ∼63-kDa pro form of FLAG/MT1-MMP alone (lane 4). The anti-FLAG mAb did not react with wild-type MT1-MMP (lane 3). (C) Western blot analysis of MT1-MMP in transiently transfected COS-1 cells or HT-1080 cells. Triton X-114 extracts of COS-1 cells transfected with control (lane 1) or wild-type MT1-MMP expression vectors and incubated in the absence or presence of 5 μM BB-94 (lanes 2 and 3, respectively) were compared with extracts of HT-1080 cells (lane 4) by immunoblotting with MT1-MMP hemopexin domain–specific polyclonal antisera. The three arrowheads indicate the positions of the putative ∼63-kDa pro form, ∼60-kDa mature form, and ∼45-kDa truncated form of MT1-MMP. COS-1 cell extracts pre-pared from cells transiently transfected with control (lanes 5 and 7) or MT1-MMP (lanes 6 and 8) expression vectors were analyzed by immunoblotting in a tandem manner with hemopexin domain–specific polyclonal antisera or anti-catalytic domain mAb, respectively.