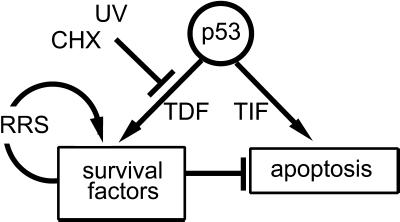
Figure 8.
In this model, the apoptosis-promoting functions of high levels of functional p53 are balanced by the p53-mediated transactivation of survival factors. When expression of these survival factors is attenuated by either UV light or CHX, p53 will induce transactivation-independent apoptosis. In addition, p53 expression before UV irradiation increases the efficiency of survival-promoting functions such as the recovery of mRNA synthesis. We also suggest that previous expression of p53 protects cells against UV- or CHX-induced apoptosis by increasing the expression of p53-regulated survival-promoting factors before cellular stress. These protective functions are not fully independent because stimulating the recovery of transcription after UV irradiation will also permit the recovery of post-UV expression of p53-regulated survival factors, thus decreasing the induction of apoptosis. TDF, transactivation-dependent function; TIF, transactivation-independent function; RRS, recovery of mRNA synthesis.