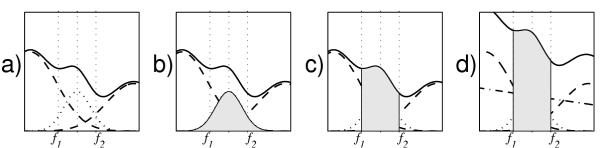
Figure 20.
Distinction between a spectral power integral from f1 to f2, and power actually carried by structures of frequencies centered between f1 and f2. Plot a) presents spectral power (versus frequency) of hypothetical structures with frequency centers lying inside (dotted) and outside (dashed line) the f1-f2 interval. Due to the uncertainty principle, their spectral contents overlap. Solid line presents their sum, i.e. total spectral power, as estimated e.g. by Fourier transform. In b) the actual power carried by structure of frequency originating between f1 and f2, as estimated in the proposed approach, is shaded. Plot c) highlights the power obtained from a spectral integral from f1 to f2. Finally in d) additional background (dotted-dashed line) is added. We observe that neighboring structures from outside the interval of interest may contribute significantly to the power estimated within the interval, and can even shift the actual position of the spectral peak related to the relevant structure (dotted line), while some of the power carried by the structure inside the interval of interest falls outside and does not contribute to the spectral integral