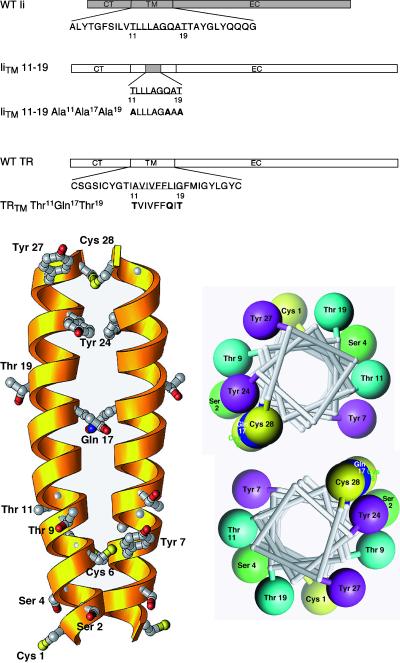
Figure 1.
(A) Schematic diagram of the TRTM mutants. A schematic diagram is shown of the MHC class II Ii showing the wild-type TM sequence. The IiTM 11–19 chimera contains a nine-amino acid substitution (shaded area) from the Ii that promotes lysosomal targeting (Kang et al., 1998). All other portions of this chimera are derived from the wild-type TR (unshaded areas). For each of the TM mutants prepared, the amino acid substitutions are shown. Constructs are referred to throughout by the corresponding names shown on the left. (B) Structural models for the TR dimeric TM. Left, three-dimensional ribbon model of the TM of the TRTM Thr11Gln17Thr19 mutant, represented as a helical dimer with the carboxy-terminus at the top. Only side chains of polar residues are depicted. The numbering system shown is the same as that used in Figure 1. Right, helical wheel representation of the same dimer, viewed from the carboxy-terminal end of the helix. Only polar residues are depicted. The software program Ribbons 3.1 was used (Carson, 1997).