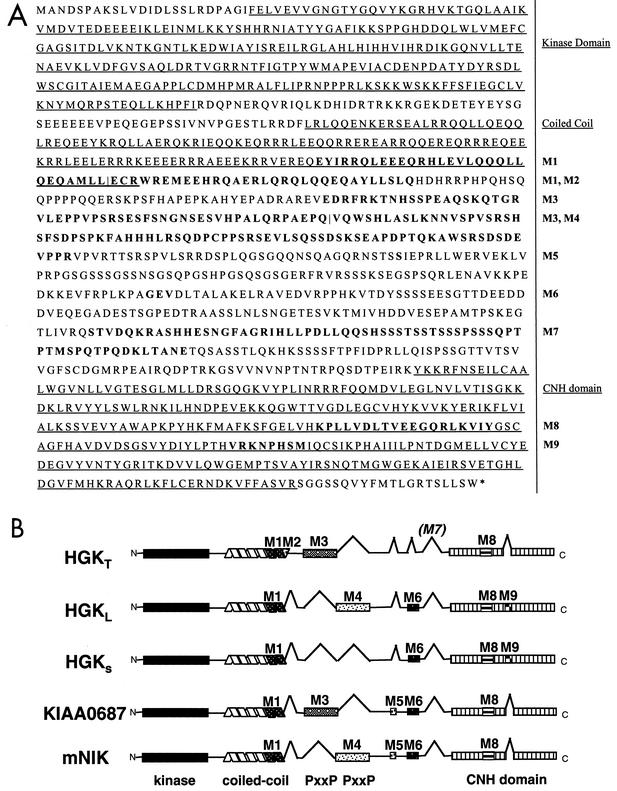
FIG. 1.
(A) HGK amino acid sequence: predicted maximal HGK protein containing all possible alternatively spliced modules. The kinase domain, the coiled-coil domain, and the CNH domain are underlined. Alternatively spliced modules M1 to M9 are shown in bold and labeled to the right of the sequence. For adjacent modules M1/M2 and M3/M4, a vertical line defines their boundaries. (B) Schematic illustration of the domain structure of known HGK splice variants compared with mouse NIK. Alternatively spliced modules are indicated with inverted V's when absent and alternative patterning where present. The HGK gene product that we cloned from a tumor cell line (HGKT) contains alternative modules M1, M2, M3, and M8. The two HGK cDNAs from a human macrophage library contain M1, M6, M8, and M9 (HGKS; short version) and M1, M4, M6, M8, and M9 (HGKL; long version). KIAA0687 isolated from brain has modules M1, M3, M5, M6, and M8. The mouse NIK clone contains M1, M4, M5, M6, and M8.