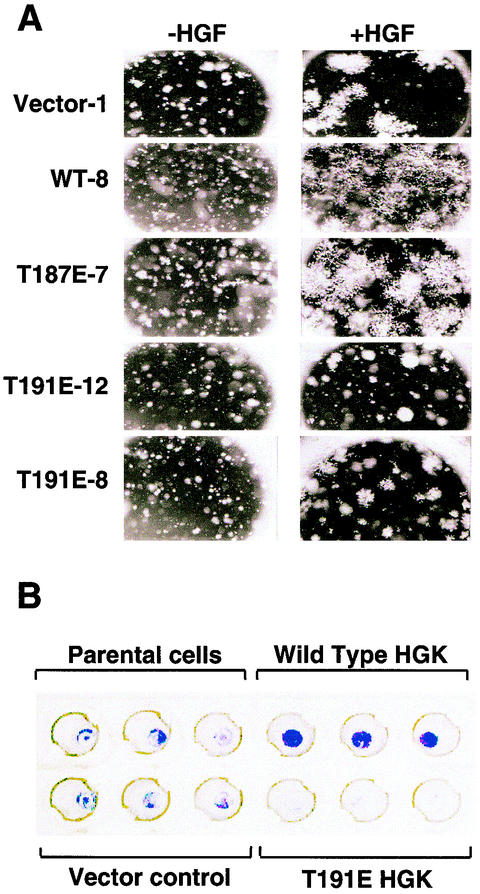
FIG. 10.
(A) Role for HGK in RIE cell morphogenesis. HGK kinase expression affects RIE-1 cells in a tubulogenesis assay. Shown are photomicrographs (3.2× magnification) of colonies formed in Matrigel after 6 days of growth. Each clone is shown with and without added HGF. Vector control is an RIE-1 clone with pLXSN alone. WT-8 is a clone expressing wild-type HGK. T187E-7 is a clone expressing the active HGK mutant; T191E-12 and T191E-8 are two clones expressing the inactive HGK mutant. (B) Role for HGK in RIE cell invasion. Boyden chambers in which the cells of the lower membrane are fixed and stained with crystal violet are shown. The amount of staining is proportional to the number of cells that successfully invaded through the Matrigel plug to colonize the lower membrane after stimulation with 50 ng of human HGF per ml for 4 days. Triplicate wells are shown from an experiment with RIE-1 stable pools expressing vector alone, wild-type, or inactive (T191E) HGK.