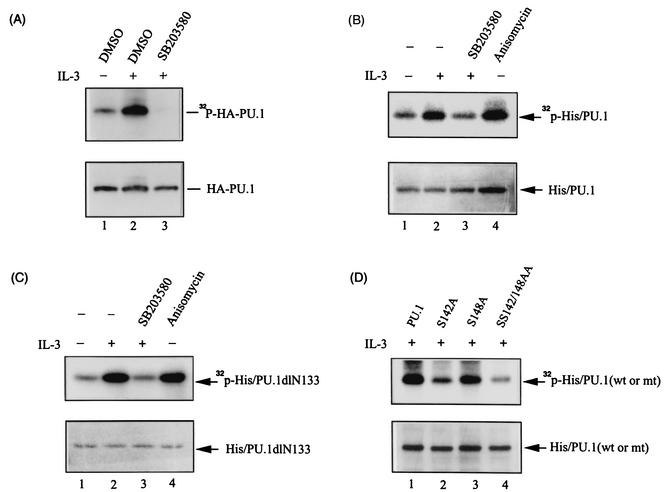
FIG. 7.
IL-3-induced phosphorylation of PU.1 occurs via a p38MAPK-dependent pathway. (A) In vivo phosphorylation of PU.1. Ba/F3-HAPU.1 cells with (lane 3) or without (lane 2) prior treatment with SB203580 were stimulated with IL-3 in the presence of [32P]orthophosphate as described in Materials and Methods. After labeling, the HA-PU.1 protein was immunoprecipitated from cell lysates by using the anti-HA antibody, resolved by SDS-PAGE, and subsequently revealed by autoradiography (top) or Western blotting with an anti-HA antibody (bottom). DMSO, dimethyl sulfoxide. (B) In vitro phosphorylation of PU.1 by the p38MAPK immunocomplex. The bacterium-produced His/PU.1 protein was phosphorylated in vitro by the p38MAPK immunocomplex as described in Materials and Methods. Lanes 1 and 2 are results of experiments with p38MAPK immunocomplexes isolated from cells without and with IL-3 treatment, respectively. Lane 3, same as lane 2, except that the p38MAPK complex was prepared from cells pretreated with SB203580 prior to IL-3 stimulation. Lane 4, same as lane 1, except that the p38MAPK complex was isolated from cells pretreated with anisomycin. (C) Same conditions as described for panel B, except that bacterium-produced His/PU.1dlN133 was used as the substrate. (D) Same conditions as described for lane 2 of panel B, except that various bacterium-produced PU.1 mutant forms, as indicated, were used as the substrate.