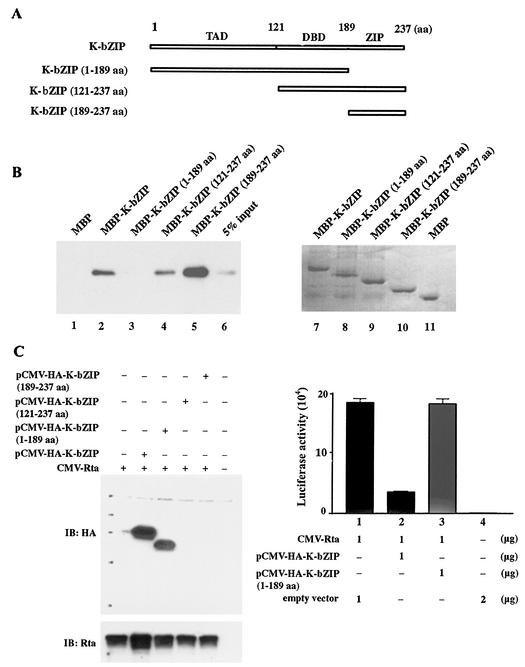
FIG. 4.
K-bZIP-Rta interaction requires the bZIP domain of K-bZIP. (A) Domain organization of K-bZIP. Regions of K-bZIP included in the deletion mutants are indicated. aa, amino acids. (B) The ZIP domain of K-bZIP binds Rta. The coding sequences of K-bZIP(1-189), K-bZIP(121-237), and K-bZIP(189-237) were derived by PCR using the respective forward primers 5′-GCCGAATTC(EcoRI)ATGCCCAGAATGA-3′, 5′-GCCGAATTC (EcoRI)ATGCAGCTTCCAACT-3′, and 5′-GCCGAATTC(EcoRI) ATGCAGGCATTAGA-3′ and the reverse primers 5′-CGGGATCC(BamHI)TCAACATGGTGGGA-3′ [K-bZIP(121-237) and K-bZIP(189-237)] and 5′-CGGGATCC(BamHI)TCACTGCTGCAGCT-3′ [K-bZIP(1-189)] and fused to the MBP sequence as described for Fig. 3. MBP and MBP fusion proteins containing full-length K-bZIP and the three deletions were expressed and purified (lanes 7 to 11, stained with Coomassie brilliant blue), and 5 μg of each was used together with 2 μg of purified Rta protein in pull-down experiments (lanes 1 to 6, Rta immunoblot) as described for Fig. 3B. (C) K-bZIP lacking the ZIP domain failed to suppress Rta transactivation. Transient transfection of HEK 293 cells and luciferase assays were performed as described for Fig. 1 except that 1 μg each of pCMV-HA-K-bZIP, pCMV-HA-K-bZIP (encoding residues 1 to 189), pCMV-HA-K-bZIP (residues 121 to 237), and pCMV-HA-K-bZIP (residues 189 to 237) were used, respectively, together with 1 μg of CMV-Rta. The expression plasmids for the deletion mutants of HA-K-bZIP were constructed by fusing their respective coding sequences (PCR derived) with the coding region of the HA epitope in pCMV-HA (Invitrogen Corp.) via EcoRI and BamHI site. The forward primers used here were 5′-GCCGAATTC(EcoRI)TGCCCAGAATGA-3′ [K-bZIP(1-189)], 5′-GCCGAATTC(EcoRI)TGCAGCTTCCAACT-3′ [K-bZIP(121-237)], 5′-GCCGAATTC(EcoRI)TGCAGGCATTAGA-3′ [K-bZIP(189-237)]. The reverse primers were as described for the MBP fusion constructs in Fig. 3. Twenty micrograms of total cell proteins from each transfection was resolved in an SDS-12% polyacrylamide gel and immunoblotted (IB) with an anti-HA mouse monoclonal antibody and a rabbit polyclonal antibody against Rta. Luciferase assays were carried out as described for Fig. 1A.