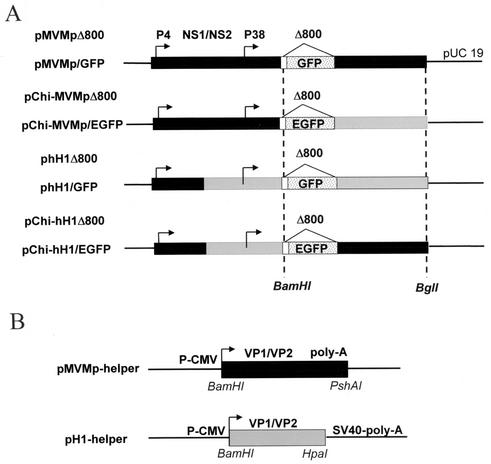
FIG. 1.
Structures of standard MVMp- and hH1-based vectors, derived chimeras, and helper plasmids. (A) The standard parvoviral vectors were derived from the modified infectious DNA clones (pMVMp and phH1) by deleting about 800 bp from the coding sequence of the structural VP1 and VP2 capsid genes and inserting a MCS (white box) at the VP2 translation initiation codon. Both promoters (P4 and P38) are indicated by arrows. The region encoding the nonstructural proteins (NS1/NS2) is shown. Chimeric MVMp-based vector DNA was constructed by replacing a BamHI-BglI fragment from pMVMpΔ800 with the corresponding region of phH1Δ800, resulting in pChi-MVMpΔ800. Chimeric hH1-based vector DNA was obtained by inserting the BamHI-BglI fragment of MVMpΔ800 into phH1Δ800 cleaved with the same restriction enzymes, resulting in pChi-hH1Δ800. The MVMp (black boxes) and hH1 (grey boxes) DNA sequences are indicated. GFP or EGFP was cloned in standard (pMVMp/GFP and phH1/GFP) and chimeric (pChi-MVMp/EGFP and pChi-hH1/EGFP) DNA vectors by inserting a 731-bp NotI restriction fragment from plasmid pTR/UF2 (30) or a 784-bp SacI-NotI restriction fragment from plasmid pEGFP-1 (Clontech), respectively, into the vectors digested with the same restriction enzymes. (B) DNA helper constructs. The VP1 and VP2 genes from either MVMp or H-1 virus are expressed under the control of the immediate-early promoter of human CMV (P-CMV). Recombinant parvoviruses were produced by cotransfection of human 293T cells with the vector DNA and helper plasmid as indicated in the text. SV40, simian virus 40.