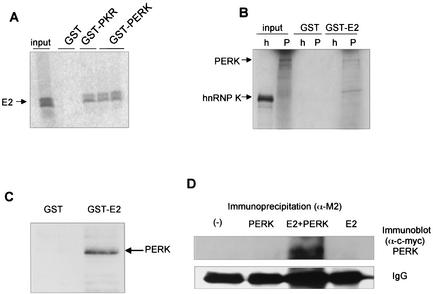
FIG. 1.
E2 binds to PERK in vitro. (A) In vitro-translated, 35S-labeled E2 was incubated with GST, GST-PKR, or GST-PERK fusion protein bound to glutathione beads. Bound proteins were separated by SDS-PAGE and visualized by autoradiography. (B) In vitro-translated, 35S-labeled full-length PERK (P) or hnRNPK (h) was incubated with GST or GST-E2 fusion proteins bound to glutathione beads. Input represents 10% of the input volume of in vitro translation products used for the binding reactions. hnRNPK (small nuclear RNA binding protein K) was used as a negative binding control. (C) HEK 293 cells were transfected with PERK-c-Myc. The cell lysate was incubated with GST- or GST-E2 bound to glutathione beads. Beads were washed, and bound proteins were eluted and separated by SDS-PAGE. Western blot transfers were probed with anti-c-Myc antibodies, and proteins were visualized by chemiluminescence. (D) Coimmunoprecipitation assay. HEK 293 cells were transfected with PERK-c-Myc, E2-flag, or both PERK-c-Myc and E2-flag. Cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with anti-Flag M2 agarose beads (Sigma) for immunoprecipitation of E2 and separated by SDS-PAGE. Western blot transfers were probed with anti-c-Myc antibodies for detection of coimmunoprecipitated PERK, and proteins were visualized by chemiluminescence. Mouse heavy chain of the antibody used for immunoprecipitation is shown as a gel loading control.