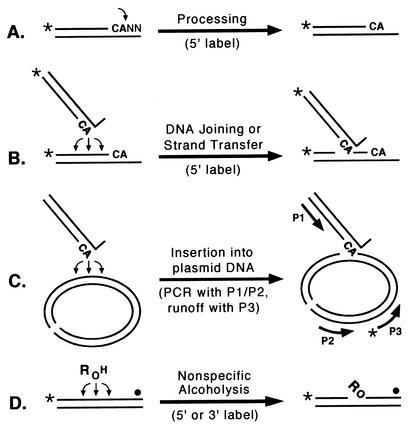
FIG. 1.
Integrase assays. The names of the assays are shown above the horizontal arrows, and the key aspects of the readouts (e.g., the position of the radiolabel or the pairing of PCR primers) are shown below the arrows. The CA bases near the 3′ ends of viral DNA are shown in boldface, the terminal nucleotides are indicated by NN, asterisks or solid circles indicate 32P groups, and P1, P2, and P3 refer to primers. (A) Processing, during which integrase makes a site-specific nick to form a labeled product two nucleotides shorter than the substrate. (B) DNA joining or strand transfer, during which integrase inserts processed viral DNA ends into any of various sites on either DNA strand to yield labeled products longer than the substrate. (C) Insertion, during which integrase inserts processed viral DNA ends into any of various sites in plasmid DNA (which is shown in its linear form); the joined products are then identified by PCR with primers P1 and P2, followed by a nested runoff reaction with 5′-radiolabeled primer P3. (D) Nonspecific alcoholysis, during which integrase uses certain nucleophilic alcohols (shown as ROH) to nick nonviral DNA at any of various sites; the labeled products will be simple oligonucleotides if the substrate is labeled at the 5′ end but will have attached R groups if the substrate is labeled near the 3′ end.