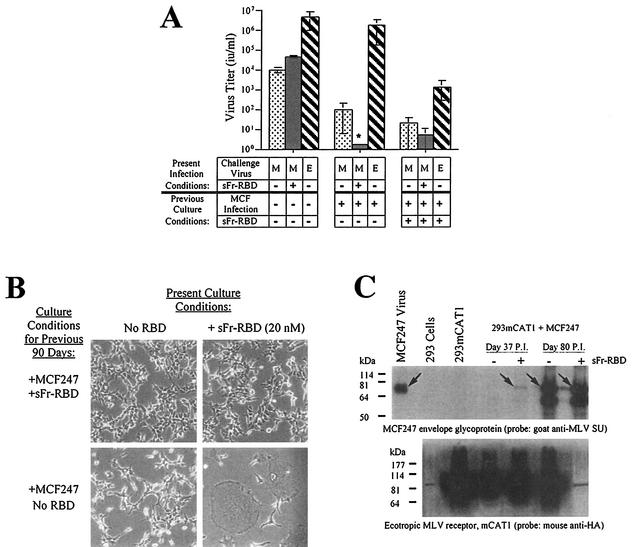
FIG. 4.
Properties of human 293mCAT1 cells chronically infected with MCF247 virus in the presence or absence of trans activation by sFr-RBD. (A) Susceptibility to virus infection. Chronically MCF247 virus-infected human 293mCAT1 cells (80 days) were challenged with MCF247 (M) or ecotropic Friend (E) viral vectors containing E. coli lacZ as indicated. An MCF247 virus challenge was also conducted in the presence of the sFr-RBD (40 nM). Two days after the challenge, infection was scored (i.u. per milliliter) by counting the foci of cells expressing β-galactosidase. The asterisk indicates that the MCF247 virus infection could not be accurately determined because of widespread cell-cell fusion after exposure to sFr-RBD (see the text and panel B). (B) Effect of sFr-RBD. Side-by-side plates of chronically infected cells (90 days) previously cultured in the presence (top panels) or absence (bottom panels) of trans activation conditions were examined 24 h after addition of sFr-RBD (20 nM) to the culture medium (right panels). Photomicrographs were prepared by phase-contrast microscopy (magnification, 200×) (C) Virus envelope glycoprotein and mCAT1 receptor expression. The steady-state levels of the MCF247 virus envelope glycoprotein and mCAT1 receptor were measured by immunoblotting of lysates prepared from MCF247 virus-infected 293mCAT1 cells. Lysates were prepared 37 and 80 days after infection. Day 37 corresponds to one passage prior to detectable cell-cell fusion by the sFr-RBD-treated cells. At day 80, the sFr-RBD-treated (+) and control (−) cultures were populated by cells that survived the preceding period of cell-cell fusion. The immunoblots were prepared after sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and probed with goat antibody that recognizes the virus envelope glycoprotein SU (top panel) or a mouse antibody, 12CA5, that recognizes the influenza virus-derived epitope tag attached at the COOH terminus of the mCAT1 receptor (bottom panel). The position of the mature MCF247 envelope glycoprotein is indicated by arrows in the top panel. In the lower panel, mCAT1 is detected as a smear from 60 to 200 kDa due to extensive glycosylation of the protein. Samples were loaded in every other lane in the same order for both blots, as indicated above the top blot, and blots were overexposed to detect low levels of protein expression. The signal present in unloaded lanes represents spillover from adjacent lanes, and the discrete band corresponding to 85 kDa in the lane containing the day 80, sFr-RBD-treated (+) lysate on the blot probed with anti-hemagglutinin is a ubiquitous cross-reacting species also seen in 293 cells without mCAT1. Molecular size markers are shown on the left.