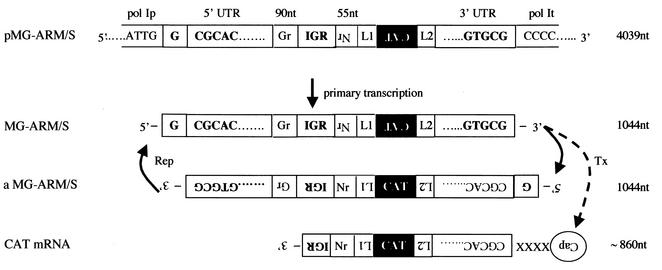
FIG. 1.
Schematic of the pol-I-driven LCMV MG, showing also transcription and replication intermediates. pMG-ARM/S contains the elements described for the MG-ARM/S construct (14) flanked by the murine pol-I promoter (pol Ip) and terminator sequences (pol It) of pRF42 (9). Transcription of pMG-ARM/S by the cellular pol-I (primary transcription) generates MG-ARM/S RNA (MG), detectable by a CAT sense riboprobe. Replication of the MG (solid right arrow) yields an aMG RNA, detectable by a CAT antisense riboprobe. This aMG serves as a template for synthesis of more MG RNA by the virus polymerase (replication [Rep]; solid left arrow). Both MG and aMG RNA species are assumed to have a nontemplated G at their 5′ ends (12). Transcription (Tx; dashed arrow) of the MG RNA by the virus polymerase yields a subgenomic-length CAT mRNA that terminates within the IGR and that is detectable by a CAT antisense riboprobe. Subgenomic mRNA species are assumed to have 5′ end cap structures, containing 4 or 5 nt not derived from viral template sequences (XXXX) (20). cis-Acting sequences are in bold. IGR, intergenic region; Gr and Nr, sequences within the GP and NP ORFs, respectively.