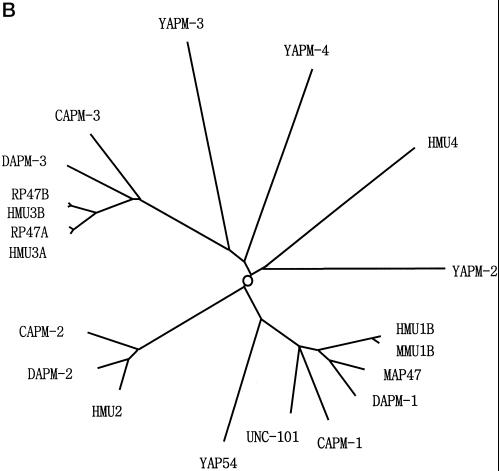
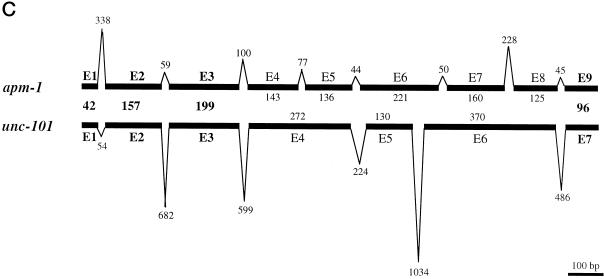
Figure 1.
(A) Comparison of amino acid sequences of APM-1, UNC-101, APM-2, and mouse AP47. The amino acids that are conserved in the three APM-1 homologs are in bold and shaded letters, and the asterisks underneath the sequences represent the amino acids conserved in all four proteins. Some of the amino acids are conserved in all four proteins, but others are conserved only in the AP-1 medium chains. (B) Diagram showing the evolutionary relationship among medium chains of clathrin AP complexes. Medium chains of all four types of complexes are compared. The circle on the center indicates a hypothetical ancestral medium chain gene. The prefix C indicates the sequence is from C. elegans, H from humans, R from rat, M from mouse, D from Drosophila, Y from yeast. For example, CAPM-1 is C. elegans APM-1 and DAPM-1 is the Drosophila APM-1 homolog. This dendrogram clearly shows that APM-1 is a member of the AP-1 medium chain family, together with UNC-101. (C) Genomic structures of the apm-1 and unc-101 genes. Exons are drawn as thick lines, and introns are drawn as thin lines outside the exon structures. Introns are not drawn in scale. The numbers indicate the numbers of nucleotides in each exon or intron.