Figure 1.
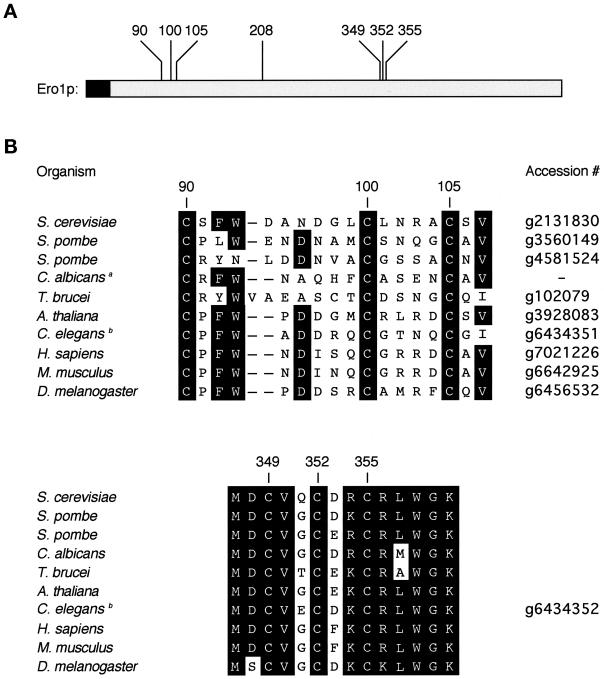
Conserved cysteines in Ero1. (A) Seven cysteines are absolutely conserved among the eukaryotic sequence homologues of Ero1. These residues are at positions 90, 100, 105, 208, 349, 352, and 355 of the primary amino acid sequence of yeast Ero1p. The N-terminal hydrophobic sequence of Ero1p (shaded) is likely to serve as a membrane anchor or signal sequence. (B) Predicted amino acid sequences of the homologues of Ero1. The regions shown correspond to residues 90–107 and 347–357 of yeast Ero1p. aThe Candida albicans sequence is derived from an unfinished genome (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Microb_blast/unfinishedgenome.html). bIn the Caenorhabditis elegans genome, two adjacent sequences are predicted to specify proteins homologous to the N- and C-terminal portions of yeast Ero1p. It remains to be determined whether these sequences correspond to one or two genes.