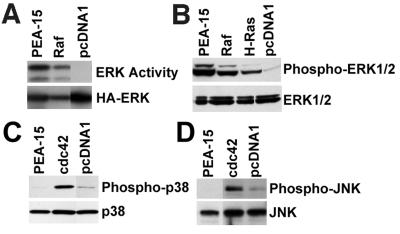
Figure 2.
PEA-15 activates the MAP kinase pathway. (A) αβpy-Cells were cotransfected with HA-ERK2 (2 μg) in combination with vector lacking an insert (3 μg) or encoding PEA-15 or RafCAAX (Raf). The transfected ERK2 was immunoprecipitated and its activity determined by its phosphorylation of myelin basic protein. Top, activity of transfected HA-ERK2. Bottom, immunoblots with anti-HA antibody 12CA5 indicate PEA-15 increases HA-ERK2 activity rather than its abundance. (B) CHO cells were transfected with 3 μg of PEA-15, RafCAAX (Raf), H-RasG12V (H-Ras), or pcDNA1. Cell lysates were analyzed by SDS-PAGE followed by immunoblotting. Top, immunoblot with a polyclonal antibody specific for phosphorylated active ERK1 and ERK2. Note that PEA-15 activates endogenous ERK1 and ERK2 to a comparable extent as RafCAAX and H-RasG12V. Bottom, immunoblot with polyclonal antibodies specific for ERK1 and ERK2. Note that endogenous ERK1/2 expression levels were similar in each transfection. (C and D) CHO cells were transfected with 3 μg of PEA-15, Cdc42, or control vector lacking an insert (pcDNA1). Cell lysates were immunoblotted by using polyclonal antibodies specific for phosphorylated p38 (C, top) or phosphorylated JNK (D, top). Alternatively, lysates were blotted with antibodies specific for p38 (C, bottom) or JNK (D, bottom) to verify similar expression levels. Note that PEA-15 does not cause phosphorylation of p38 or JNK. As a control, Cdc42 activates both p38 and JNK.