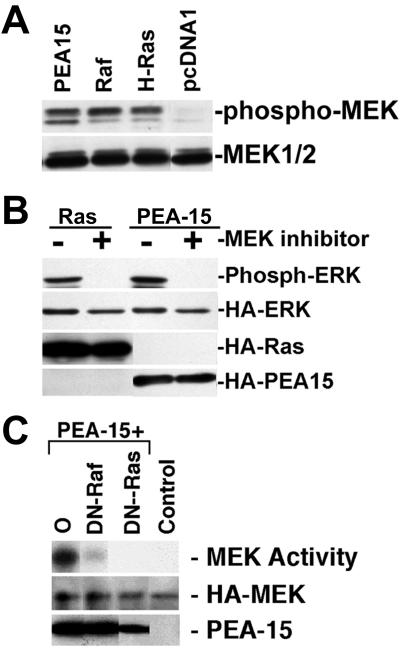
Figure 3.
PEA-15 activates MEK in a Ras-dependent manner. (A) αβpy-Cells were cotransfected with HA-ERK (2 μg) and PEA-15 (3 μg) or RasG12V (3 μg). Twenty-four hours after transfection, 50 μM U0126 MEK inhibitor dissolved in dimethyl sulfoxide was added. Dimethyl sulfoxide alone was added to control plates. Cell lysates were analyzed by SDS-PAGE followed by immunoblotting. Top, immunoblot with a polyclonal antibody specific for phosphorylated active ERK1/2. Activity of transfected ERK is shown. Bottom three gels, immunoblots with monoclonal antibody 12CA5 to the HA epitope tag. Expression levels of HA-ERK, RasG12V, and PEA-15 were equal in treated versus untreated cells. (B) αβpy-Cells were transfected with HA-MEK2 (2 μg) in combination with pcDNA1 (6 μg) (Control). In separate plates, cells were transfected with HA-MEK2 (2 μg) and PEA-15 (3 μg) in combination with pcDNA1 (O; 2 μg), RafN4 (DN-Raf; 2 μg), or RasT17N (DN-Ras; 1 μg). Transfected HA-MEK2 was immunoprecipitated with anti-HA antibody, 12CA5, and MEK2 activity was determined by its capacity to phosphorylate GST-ERK2 as described under MATERIALS AND METHODS. Top, note that dominant-negative constructs of both Raf and Ras impair the capacity of PEA-15 to activate MEK2. Middle, immunoblot with anti-HA antibody 12CA5 indicates similar MEK2 expression levels in all transfections. Bottom, PEA-15 is overexpressed in each transfection as detected by immunoblotting.