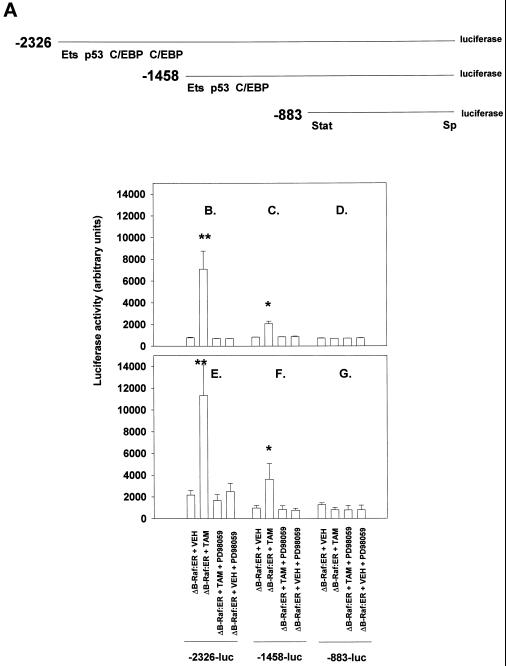
Figure 3.
MAPK-dependent modulation of p21-promoter activity in primary hepatocytes and Hep G2 cells. (A) Schematic diagram showing the p21 promoter, the deletions used in this study, and putative p53, Ets, and C/EBP transcription factor binding sites within the promoter. MAPK-dependent modulation of p21-promoter activity in primary hepatocytes and Hep G2 cells. (B) -2326 full-length p21-promoter in primary hepatocytes. (C) -1458 truncated p21-promoter in primary hepatocytes. (D) -883 truncated p21-promoter in primary hepatocytes. (E) -2326 full-length p21-promoter in Hep G2 cells. (F) -1458 truncated p21-promoter in Hep G2 cells. (G) -883 truncated p21-promoter in HepG2 cells; hepatocytes were infected with kinase active ΔB-Raf:ER poly-L-lysine adenovirus (250 m.o.i.), followed by culture as in Methods. In some experiments and in addition to ΔB-Raf:ER infection, cells were also infected with plasmids containing either full-length p21-promoter or a truncated p21-promoters (containing the initiating ATG proximal 883 or 1458 bp) poly-L-lysine adenovirus (at 100 m.o.i. each). After 24 h to allow protein expression, hepatocytes were treated with either vehicle control or with 100 nM 4-hydroxytamoxifen, and with or without 50 μM PD98059, for 480 min and luciferase activity determined as in Methods (n = 8 ± SEM). ** p < 0.001 greater than non-TAM treated control value; *p < 0.05 greater than non-TAM treated control value.