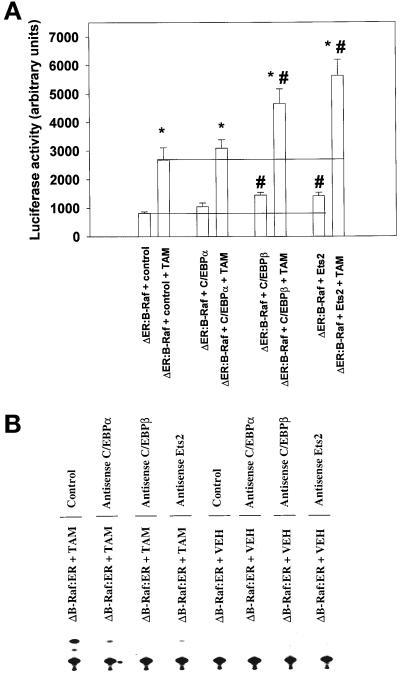
Figure 5.
Overexpression of transcription factors enhances MAPK-dependent activation of the p21 promoter. (A) Overexpression of either C/EBPβ or Ets2 proteins enhances basal and MAPK-stimulated -2326 full-length p21-luciferase promoter activity. (B) Antisense C/EBPβ, and to a lesser extent antisense Ets2 and antisense C/EBPα, reduce MAPK-induced activation of the -1384/-1184 portion of the p21 promoter. Hepatocytes were infected with kinase active ΔB-Raf:ER poly-L-lysine adenovirus (250 m.o.i.), followed by culture as in Methods. In panel A, in addition to ΔB-Raf:ER infection, cells were also infected with a plasmid containing the full-length p21-promoter (100 m.o.i.). In panel A, portions of cells were also transfected with constructs to express either p42 C/EBPα, p35 C/EBPβ, or p53 Ets2; half the protein amount was used in panel A compared with data panels in Figures 4 and 5. In panel B, addition to ΔB-Raf:ER infection, cells were also infected with plasmid containing a small portion of the p21 promoter (-1383/-1184) in which exists a putative binding site (-1270/-1256) for C/EBP transcription factors; using poly-L-lysine adenovirus (at 100 m.o.i.). In panel B, cells were also infected with plasmids to express either anti sense C/EBPα or antisense C/EBPβ. In panels B and C, cells were transfected with an antisense oligonucleotide to Ets2 (10 μM, using Superfect reagent as per manufacturer's instructions; Qiagen, Valencia, CA). After 24 h to allow protein expression, hepatocytes were treated with either vehicle control or with 100 nM 4-hydroxytamoxifen, and with or without 50 μM PD98059, for 480 min and luciferase activity or CAT activity determined as in Methods. For luciferase studies (n = 8 ± SEM), *p < 0.05 greater than non-TAM treated control value; #p < 0.05 greater than corresponding control cell value. For CAT assays, representative experiments are shown (n = 10).