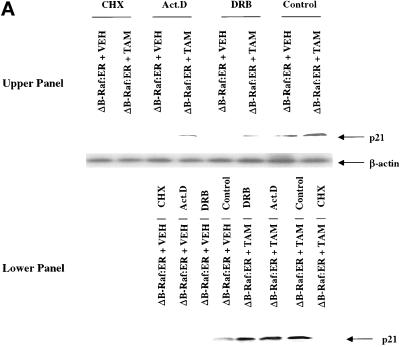
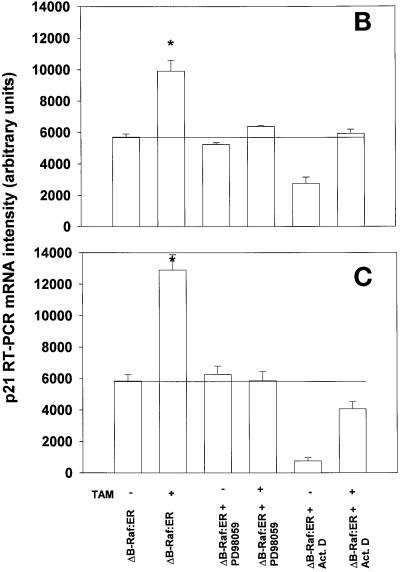
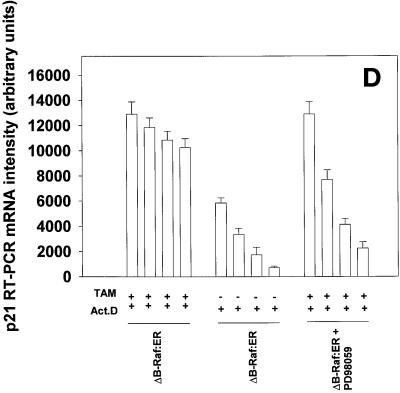
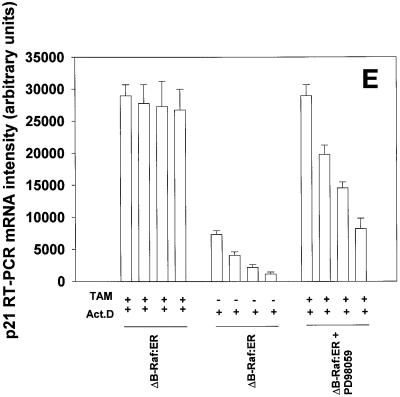
Figure 8.
Prolonged MAPK signaling increases p21 protein expression via posttranscriptional mechanisms in primary hepatocytes. (A) MAPK-dependent increases in p21 protein are blunted by inhibitors of transcription and translation. (B and C) MAPK-induced an increase in p21 mRNA levels which is blocked by inhibitors of transcription. (D and E) MAPK enhances the mRNA stability of stimulated levels of p21 mRNA. Hepatocytes were infected with kinase active ΔB-Raf:ER poly-L-lysine adenovirus (250 m.o.i.), followed by culture as in Methods. After 24 h to allow protein expression, hepatocytes were treated with either vehicle control or with 100 nM 4-hydroxytamoxifen for the indicated times. (A, upper section) Cells were treated for 8 h with 4-hydroxytamoxifen in the presence or absence of either 5 μM actinomycin D, 30 μM DRB, 20 μg/ml cycloheximide. (A, lower section) Cells were treated for 28 h with 4-hydroxytamoxifen and then for an additional 8 h with 4-hydroxytamoxifen in the presence or absence of either 5 μM Actinomycin D, 30 μM DRB, 20 μg/ml cycloheximide. The expression of p21 determined by immunoblotting. Lanes with either ΔB-Raf:ER + vehicle control (VEH) or ΔB-Raf:ER + 4-hydroxytamoxifen (TAM). A representative experiment for each condition is shown (n = 4). (B and C) Cells were treated for (B) 3 h and (C) 8 h with 4-hydroxytamoxifen in the presence or absence of 5 μM actinomycin D. RT-PCR determination of p21 mRNA was performed using specific oligonucleotides as in Methods (n = 3 ± SEM). RT-PCR was simultaneously performed on β-actin as an internal standard; p21 mRNA levels shown are normalized to the internal β-actin standard. During this time, no effect was observed on the levels of control β-actin mRNA (our unpublished data). (D and E) Cells were treated for (D) 8 h and (E) 36 h with 4-hydroxytamoxifen followed by treatment with either PD98059, Actinomycin D or both drugs and samples were taken at various times for a further 2 h, 4 h, and 6 h to determine p21 mRNA levels. RT-PCR determination of p21 mRNA was performed using specific oligonucleotides as in Methods (n = 3 ± SEM). RT-PCR was simultaneously performed on β-actin as an internal standard; p21 mRNA levels shown are normalized to the internal β-actin standard. During this time, no effect was observed on the levels of control β-actin mRNA (our unpublished data) *p < 0.05 greater than non-TAM treated control value.