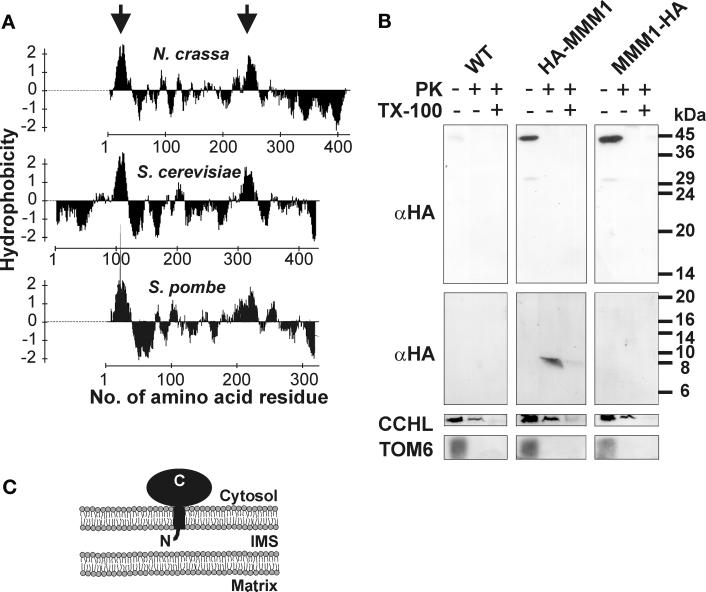
Figure 4.
Topology of MMM1 in the outer membrane. (A) Hydropathy plot of MMM1. The hydrophobicity profiles of MMM1 of N. crassa, S. cerevisiae, and S. pombe were plotted according to Kyte and Doolittle (1982). Hydrophobic regions predicted to form α-helical transmembrane segments (Hofmann and Stoffel, 1993) are indicated by arrows. (B) Submitochondrial localization of MMM1. Equal amounts of isolated mitochondria of wild-type (WT), a strain expressing an N-terminally tagged protein (HA-MMM1), and a strain expressing a C-terminally tagged protein (MMM1-HA) were treated with 100 μg/ml proteinase K (PK) in the presence or absence of 0.25% Triton X-100 (TX-100) for 15 min on ice, or were left untreated. Proteins were precipitated with trichloroacetic acid and analyzed by immunoblotting. The upper panel shows a Western blot of a standard SDS-PAGE, the lower three panels show Western blots of high Tris-urea gels that allow a better separation of low-molecular-weight proteins or fragments. The upper two panels were decorated with monoclonal antibodies recognizing the HA epitope tag (αHA) present on HA-MMM1 and MMM1-HA. Faint bands are due to cross reactivity of the HA antibody. Molecular size markers are indicated at the right. Polyclonal antiserum against cytochrome c heme lyase (CCHL), a soluble intermembrane space protein (Mayer et al., 1995), was used as a control for opening of the outer membrane, and polyclonal antiserum against TOM6, a protein of the outer membrane (Rapaport et al., 1998), was used as a control for protease treatment of intact mitochondria and for blotting of small hydrophobic proteins. (C) Topology of MMM1 in the mitochondrial outer membrane. IMS, intermembrane space; N, N terminus of MMM1; C, C terminus of MMM1.