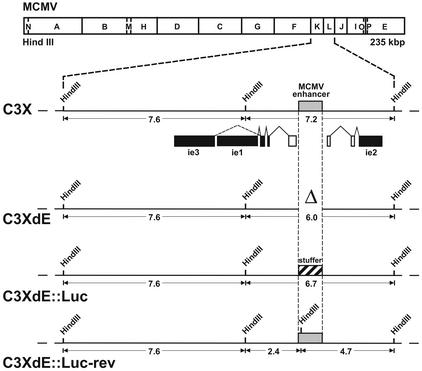
FIG. 1.
Construction of enhancerless MCMV BAC genomes. The HindIII map of the MCMV genome is shown at the top. The HindIII K and L fragments from the parental MCMV BAC genome, C3X, are expanded below to show the major IE gene region. The structures of the ie1, ie2, and ie3 transcripts are indicated below the expanded map. Coding exons are shown solid, and the first noncoding exons of the ie1-ie3 and ie2 transcription units are depicted as open rectangles. The shaded box marks the MCMV enhancer ie1-ie3 promoter. The recombinant MCMV BAC plasmids C3XdE, C3XdE::Luc, and C3XdE::Luc-rev, shown below the C3X genome, were generated by successive rounds of homologous recombination in E. coli starting from the parental BAC plasmid C3X (for C3XdE and C3XdE::Luc) or C3XdE::Luc (for C3XdE::Luc-rev), as indicated in Materials and Methods. The MCMV BAC plasmid C3XdE contains a 1.1-kbp deletion within the HindIII L fragment extending from nucleotide position −48 to −1191 relative to the ie1-ie3 MCMV transcription start site. C3XdE::Luc contains a 770-bp fragment from the luciferase gene replacing nucleotide sequences from −48 to −1191 of the MCMV MIEP enhancer region. C3XdE::Luc-rev is a revertant of C3XdE:: Luc in which the enhancer sequences were reconstituted. The 1.1-kbp deletion in the enhancer region is marked Δ. The crosshatched box represents the luciferase stuffer region. The sizes of the natural and new HindIII K and L fragments are indicated. The illustration is not drawn to scale.