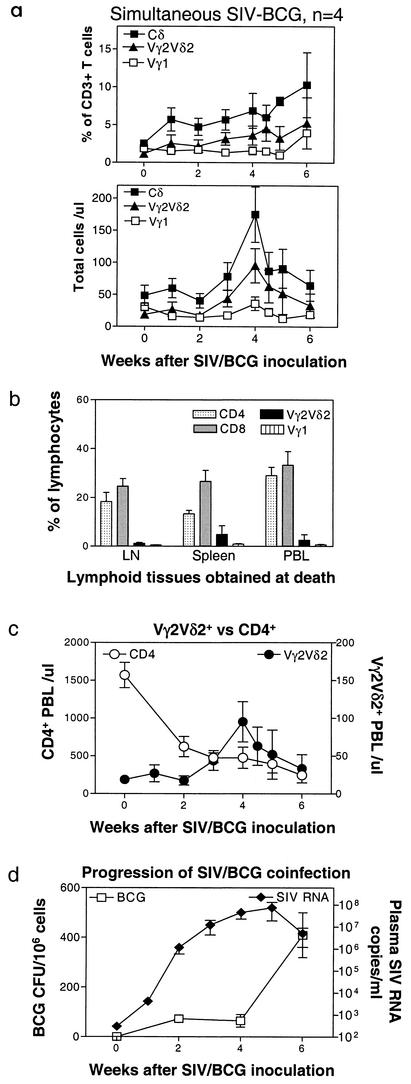
FIG. 2.
Naïve monkeys coinfected simultaneously with SIVmac and BCG did not sustain an expansion of Vγ2Vδ2+ T cells. Data at the end points were obtained from the PBL of the naïve monkeys at the time that these animals developed a fatal tuberculosis-like disease. Necropsy showed SIV-related lymphoid depletion and granulomas in multiple organs, with high numbers of BCG CFU identified in lymph nodes of the SIVmac-BCG-coinfected monkeys (38). (a) Changes in the percentages and absolute numbers of CD3+ T cells that are Vγ1+or Vγ2Vδ2+ in the blood after BCG inoculation. Data shown are the means and standard errors of the means of values from four SIVmac-infected monkeys (two pigtailed and two rhesus). (b) Comparisons of CD4+, CD8+, Vγ1+, and Vγ2Vδ2+ T cells among lymph nodes, spleens, and PBL at the death of the coinfected monkeys. Numbers are percentages of gated lymphocytes as seen in flow cytometry. (c) Kinetic changes in numbers of CD4+ T cells in the blood and Vγ2Vδ2+ T cells in naïve monkeys following simultaneous SIVmac-BCG inoculation. (d) Plasma SIV RNA and BCG burdens in lymph nodes of naïve monkeys following simultaneous SIVmac and BCG inoculation.