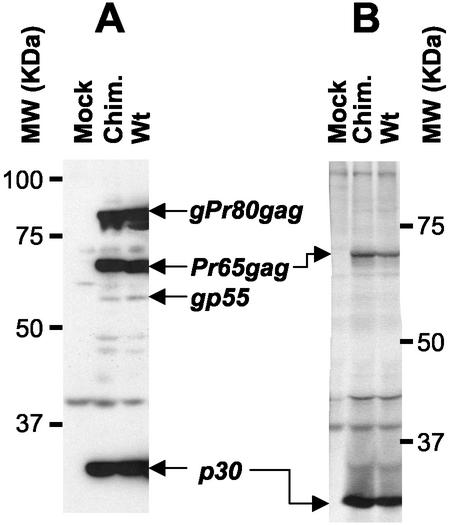
FIG. 4.
Analysis of viral proteins in chimeric viruses. (A) Chronically infected NIH 3T3 cells were lysed in RIPA buffer (10 mM sodium phosphate [pH 7.2], 140 mM NaCl, 1% Nonidet P-40, 0.5% sodium deoxycholate) containing a cocktail of protease inhibitors. Cell debris was removed by centrifugation (15,000 × g for 45 min in a Sorvall F-20 rotor at 4°C); samples of cell lysates were then analyzed by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and immunoblotting using a goat anti-p30 antiserum (National Cancer Institute) and horseradish peroxidase-conjugated swine anti-goat secondary antibody (Cedarlane). Antigen-antibody complexes were detected by enhanced chemiluminescence and autoradiography. (B) Subconfluent cells were subjected to metabolic radiolabeling (200 μCi of ICN Tran35S-Label per 10-cm-diameter petri dish); cell supernatants were collected 8 h later and clarified by centrifugation (1,000 × g for 15 min in a Sorvall SH 3000 rotor at 4°C) followed by filtration onto 0.45-μm-pore-size nitrocellulose filters. Viruses were then semipurified by ultracentrifugation of clarified supernatants through a 3-ml 20% sucrose cushion in phosphate-buffered saline for 2 h at 100,000 × g in a 70.1 rotor (Beckman) at 4°C. Pelleted viral particles were resuspended in 100 μl of RIPA buffer and centrifuged for 30 min at 15,000 ×g in a Sorvall F-20 microrotor. These samples containing viral proteins were incubated overnight at 4°C with the anti-p30 antiserum, and the immune complexes were collected by incubation with protein G-Sepharose (Amersham) for 3 h at 4°C. Sepharose beads were briefly pelleted in a microcentrifuge and washed extensively in RIPA buffer. Bound antigen-antibody complexes were analyzed on sodium dodecyl sulfate-10% polyacrylamide gels, fixed, dried, and exposed on Biomax MR films (Kodak). The positions of the molecular weight markers and selected viral proteins in the wild type (Wt) and the chimeric virus (Chim.) are indicated in both panels A and B.