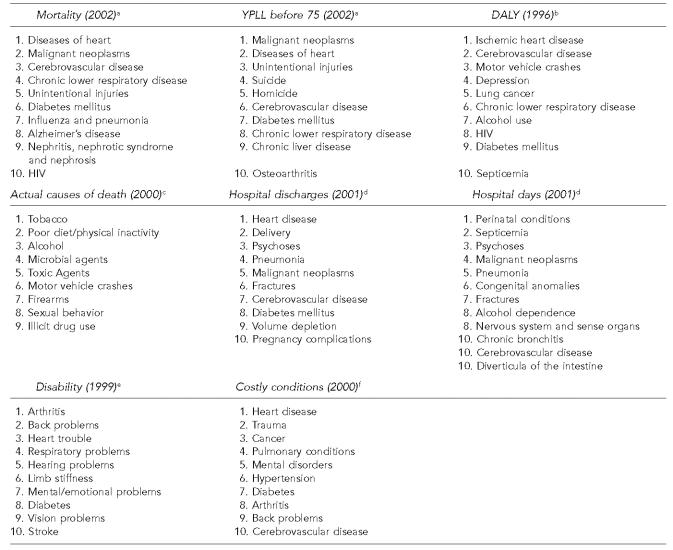
Figure.
a National Center for Health Statistics. Health, United States, 2004. Hyattsville (MD): Department of Health and Human Services, National Center for Health Statistics; 2004.
b McKenna MT, Michaud CM, Murray CJL, Marks JS. Assessing the burden of disease in the United States using disability-adjusted life years. Am J Prev Med 2005;28:415-23.
c Mokdad AH, Marks JS, Stroup DF, Gerberding JL. Actual causes of death in the United States, 2000 [published erratum appears in JAMA 2005;293:293-4]. JAMA 2004;291:1238-45.
d Kozak LJ, Owings MF, Hall MJ. National Hospital Discharge Survey: 2001 annual summary with detailed diagnosis and procedure data. Vital Health Stat 13 2004:1-198.
e Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (US). Prevalence of disabilities and associated health conditions among adults—United States, 1999 [published erratum appears in MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 2001:50(08):149]. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 2001;50(07):120-5.
f Thorpe KE, Florence CS, Joski P. Which medical conditions account for the rise in health care spending? Health Affairs (Millwood) 2004 Aug 25;Suppl Web Exclusives;W4-437-45 [cited 2005 Apr 4]. Available at: URL: http://content.healthaffairs.org
YPLL = years of potential life lost
DALY = disability-adjusted life years
Leading causes of public health burden using alternative measures of burden, United States