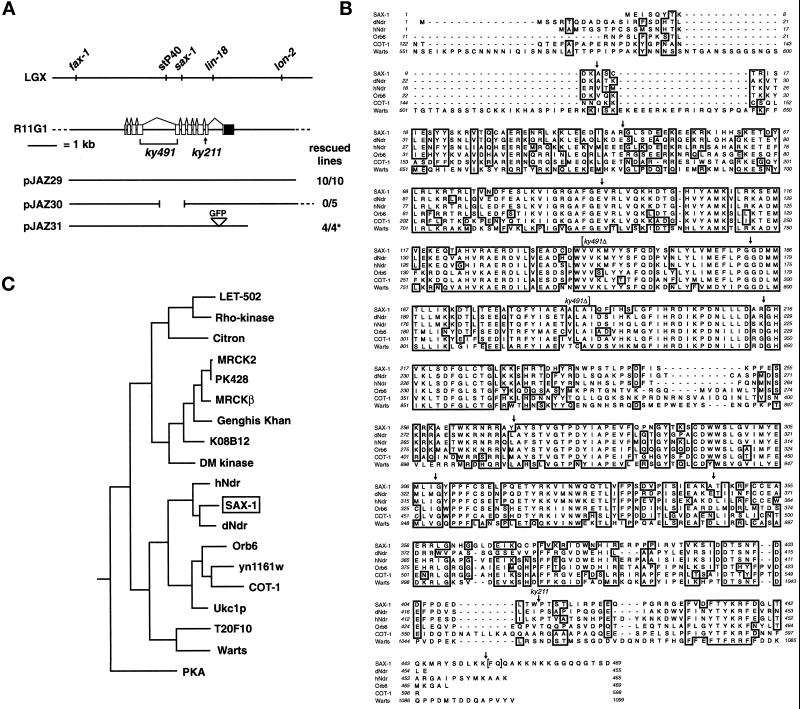
Figure 4.
sax-1 encodes a serine/threonine kinase. (A) The sax-1 mutation mapped to LGX between the stP40 and lin-18 markers. sax-1 mutant defects were rescued by the R11G1 cosmid and specific cosmid subclones. The exon/intron structure of the sax-1 genomic region is shown; exons are open boxes, introns are lines, and the 3′ UTR is a closed box. Rescued lines indicate the number of independent transgenic sax-1(ky211) lines whose defects scored with the ceh-23::gfp transgene (pJAZ29 and pJAZ30) or by DiI filling (pJAZ31) were rescued by the specified plasmid (see MATERIALS AND METHODS). The asterisk indicates that two of two sax-1(ky211) transgenic lines and two of two sax-1(ky491) transgenic lines were rescued. (B) Alignment of the SAX-1 protein sequence with sequences of the Drosophila and human Ndr kinases (dNdr and hNdr), S. pombe Orb6, Neurospora COT-1, and Drosophila Warts/Lats. Conserved residues that are shared by four or more proteins are boxed. Arrows indicate splice junctions in sax-1. Brackets denote the beginning and end of the ky491 deletion, which also causes a frame shift that results in sax-1 termination early in the kinase domain. Sequences were aligned with the use of Clustal W. (C) Phylogenetic tree indicating the relationship between the kinase catalytic domains of SAX-1 and other serine/threonine kinases. Rho-kinase is p160ROCK/rokβ. Sequences were analyzed with the use of the Phylip/PAUP Genetics Computer Group (Madison, WI) sequence analysis programs.