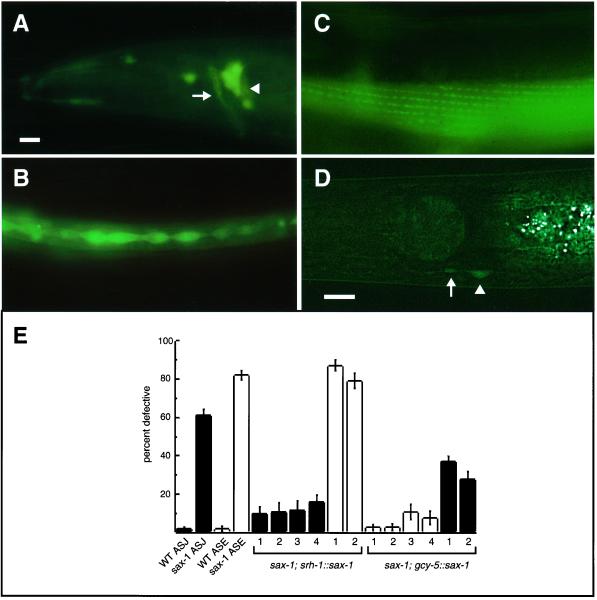
Figure 5.
SAX-1::GFP expression and site of action. SAX-1::GFP expression is shown in larval (B) and adult (A, C, and D) animals. All panels show a lateral view of one side of the animal. Anterior is to the left, dorsal at top. Bars, 10 μm. (A) SAX-1::GFP is expressed in lateral ganglion neurons in the head of the animal (arrowhead) that contribute axons to the nerve ring (arrow). (B) SAX-1::GFP labels lateral seam cells in the epidermis. (C) The SAX-1::GFP tag displays a punctate localization in muscle, shown here in body wall muscle in the midbody of the animal. This pattern is relatively common for GFP fusion genes, and its significance is unknown. (D) The srh-1::sax-1::gfp tagged fusion was detected throughout the cell body of the ASJ neuron type (arrowhead) and occasionally in the proximal axon and dendrite (arrow). (E) SAX-1 is likely to function cell autonomously in the ASJ and ASE chemosensory neurons. ASJ ectopic neurite defects are represented by black bars and ASE cell shape defects are represented by white bars. ASJ was scored with the use of DiI filling. Error bars indicate the SE of proportion; n = 46–307 animals scored for each data point. Expression of the srh-1::sax-1::gfp transgene in ASJ rescued the ASJ defects of sax-1(ky491) mutants (four independent transgenic lines) but not the ASE defects (two independent transgenic lines). Expression of the gcy-5::sax-1 transgene in ASE rescued the ASE defects of sax-1(ky491) mutants (four independent transgenic lines) and partially rescued the ASJ defects (two independent transgenic lines). All rescued lines were significantly different from sax-1(ky491) animals (p < 0.001, χ2 test).