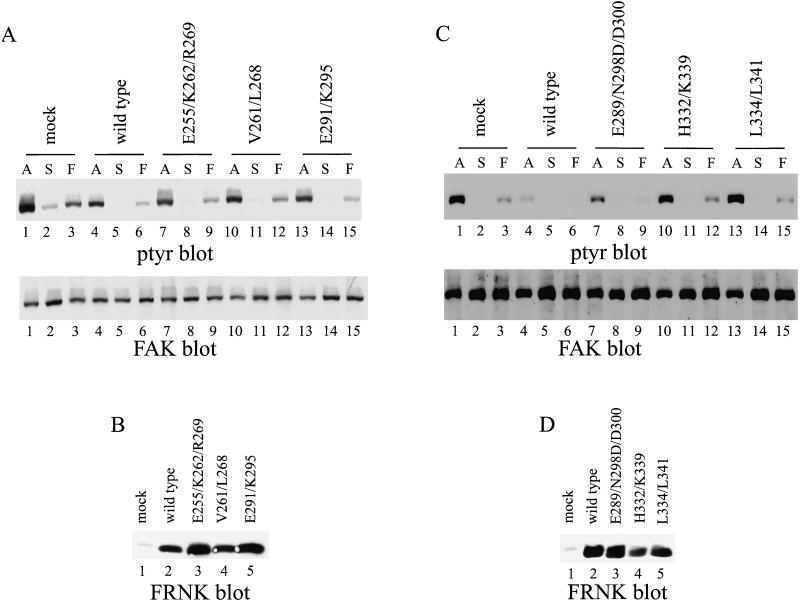
Figure 10.
Inhibition of tyrosine phosphorylation of endogenous FAK by FRNK mutants. (A and C) Control CE cells (lanes 1–3) or CE cells expressing wild-type FRNK (lanes 4–6) or FRNKE255/K262/R269 (A, lanes 7–9), FRNKV261/L268 (A, lanes 10–12), FRNKE291/K295 (A, lanes 13–15), FRNKE289/N298D/D300 (C, lanes 7–9), FRNKH332/K339 (C, lanes 10–12), or FRNKL334/L341 (C, lanes 13–15) were analyzed. Adherent cells (A) (A and C, lanes 1, 4, 7, 10, and 13) or cells held in suspension (S) (lanes 2, 5, 8, 11, and 14) or cells plated onto fibronectin (F) (lanes 3, 6, 9, 12, and 15) were lysed and endogenous FAK was immunoprecipitated by using BC2. The immune complexes were analyzed by Western blotting for phosphotyrosine (A and C, top). The blots were stripped and reprobed for FAK (A and C, bottom). (B and D) Twenty-five micrograms of cell lysate was analyzed for FRNK expression by Western blotting with BC4.