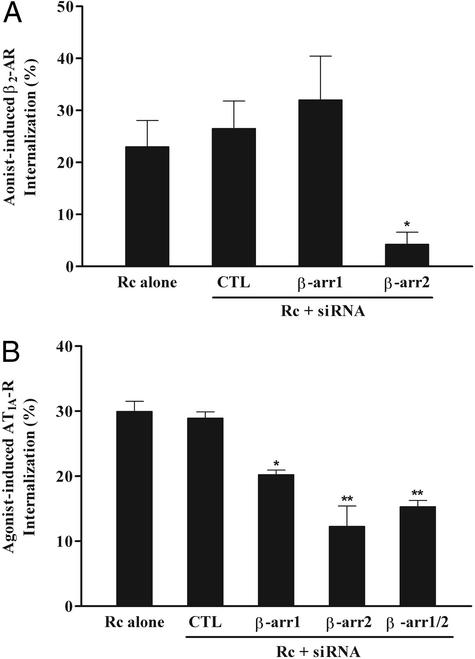
Figure 3.
Effect of siRNA-mediated suppression of β-arrestin levels on 7MS receptor internalization. (A) HEK293 cells were transfected with either control RNA (CTL) or the indicated β-arrestin siRNA and subsequently transfected again with plasmids encoding Flag epitope-tagged β2-AR as described. Serum-starved cells were exposed to 10 μM isoproterenol for 30 min at 37°C and analyzed for their plasma membrane content of the Flag epitope-tagged β2-AR by flow cytometry. Values shown are expressed as percentage of loss of agonist-induced cell surface receptors over nonstimulated cells. (B) HEK293 cells were transfected with appropriate amounts of AT1A-R encoding plasmids and the indicated siRNAs simultaneously. Receptor expression was equivalent (200–300 fmol per mg of protein) among all transfected cells. Cells were cooled down in ice-cold, serum-free media and subsequently stimulated with 0.2 nM 125I-labeled AngII for 5 min at 37°C. Percent of agonist-stimulated AT1A-R sequestration was determined as acid-resistant cpm divided by the total cpm bound. Data represent the mean ± SE from three independent experiments done in triplicate. Statistical significance was determined by using a one-way ANOVA to correct for multiple comparisons between β-arrestin siRNA-transfected cells and control cells [both receptor-transfected cells without RNA (Rc alone) and control RNA-treated cells] (*, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01).