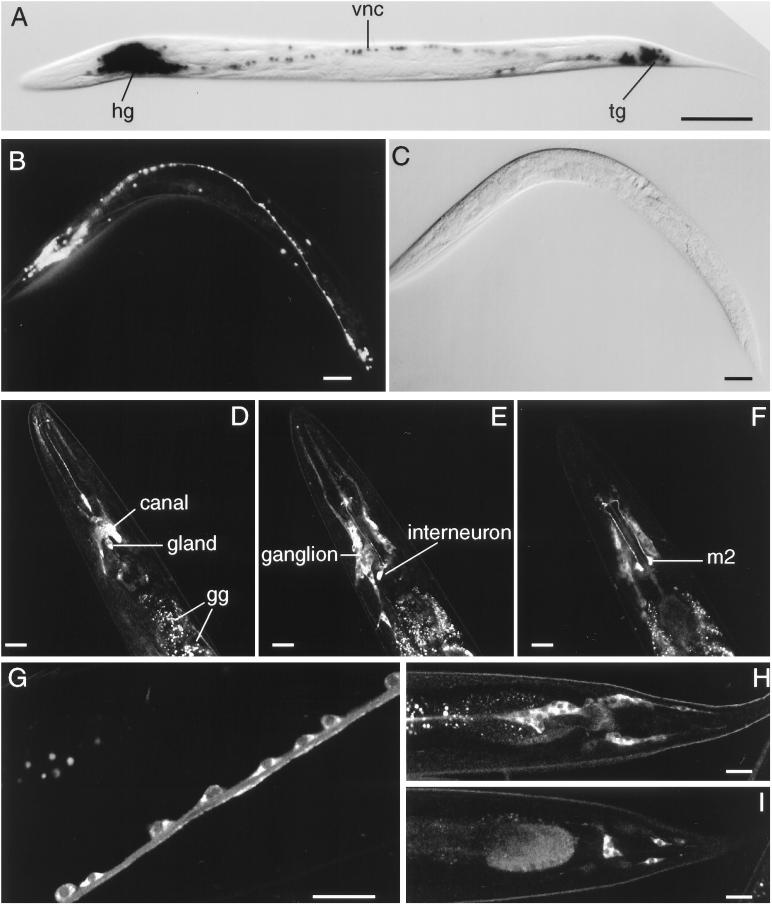
Figure 4.
(A–C) In vivo ric-19 promoter expression visualized with the use of the NLS–GFP or NLS–lacZ reporter genes. (A) NLS–lacZ staining in an animal transgenic for the array Ex[pCelicaDP-lacZ; pRF4]. (B) NLS–GFP expression in a young adult transgenic animal carrying the array Ex[pCelicaDP-GFP; pRF4]. (C) Nomarski view of panel b. hg, head ganglia; vnc, ventral nerve cord; tg, tail ganglia. Bars in A–C, 50 μm. (D–I) Confocal microscopy of transgenic animals carrying the array Ex[pRIC19::GFP; pRF4]. (D–F) Three confocal planes of the head region. In D, the excretory canal cell and gland cells are indicated; the autofluorescent gut granules (gg) are also indicated. Note the expression of the RIC-19::GFP protein in neurons of the head ganglion (most visible in E) as well as the high levels of expression in a pharyngeal interneuron (E) and m2 neurons (F). (G) A portion of the ventral nerve cord; note that the RIC-19::GFP fusion protein is expressed in the cytoplasm of each neuron shown. (H and I) Two sections of the tail region; note the expression of the RIC-19::GFP protein in the neurons of the tail ganglia. Bars in D–I, 20 μm.