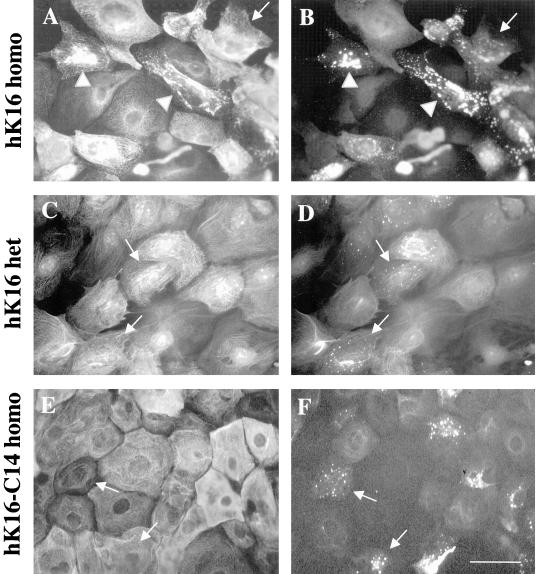
Figure 4.
Detection of nonfilamentous keratins: primary keratinocytes were grown for 72 h at 0.2 mM calcium, fixed with 100% methanol, and then coimmunostained with the K8.12 antibody and another anti-keratin antiserum. Homozygous K16 keratinocytes show K8.12 staining (B) as small punctae (arrow) or larger aggregates (arrowheads). Double-immunofluorescence by using the anti-K16 (1275) polyclonal antiserum (A) reveals that the large K8.12 aggregates (B) colocalize with reorganized keratin filaments (compare A and B). Similar analyses in heterozygous K16 (D) and homozygous K16-C14 (F) keratinocyte cultures reveal the presence of K8.12 immunostaining as small punctae only (arrows). Double-immunofluorescence by using the anti-K16 (1275) polyclonal antibody (C) or with anti-K17 antiserum (E) illustrates that keratinocytes showing reactivity with K8.12 (arrows) feature an intact keratin filament network (compare C and D; E and F). Bar, 20 μm.