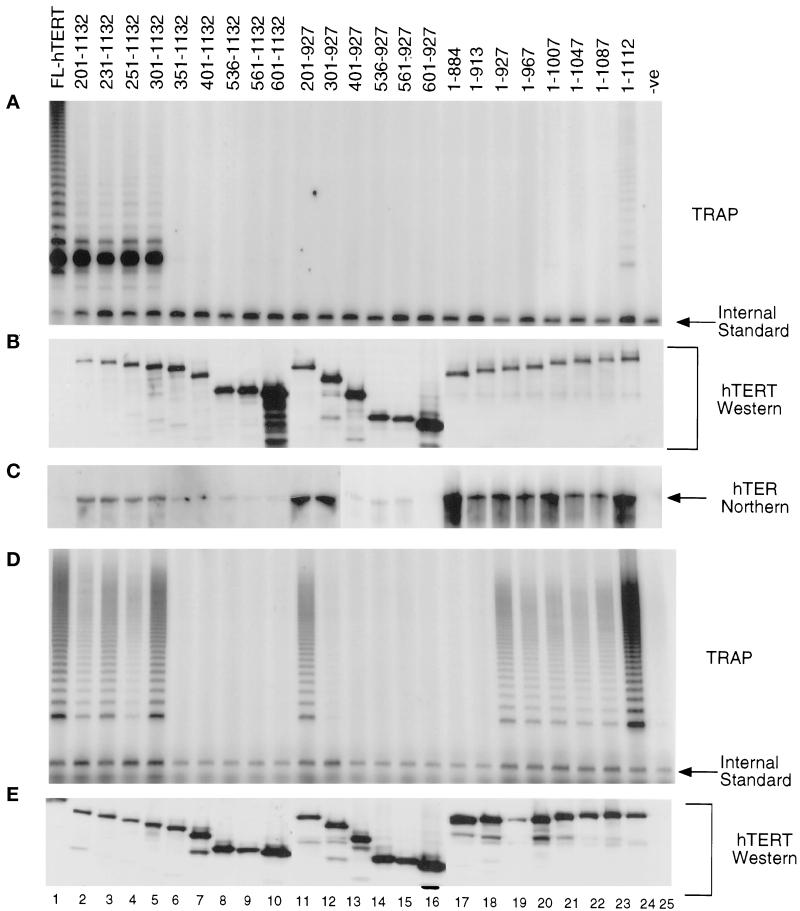
Figure 2.
Regions outside the conserved RT domain of hTERT are important for telomerase activity. Numbering refers to the positions of the amino acids of hTERT. (A) Results of telomerase assays from hTERT truncations synthesized in RRL. Different amino- and carboxy-terminal truncations of hTERT (as indicated) containing a flag epitope tag were synthesized in RRL in the presence of purified hTER, and were subjected to an anti-flag immunoprecipitation and analyzed for telomerase activity. (B) Analysis of protein production in the reticulocyte lysates by Western analysis with an α-hTERT peptide polyclonal antibody (Harrington et al., 1997b). Full-length hTERT is not visible due to low levels of the protein below the limit of detection. However, equal amounts of hTERT cDNA were added to the reticulocyte lysates and the presence of telomerase activity indicated that hTERT is present. (C) Northern blot analysis of the anti-flag immunoprecipitations of the hTERT truncations probed with an end-labeled oligonucleotide complementary to the RNA template region (see MATERIALS AND METHODS). hTER is not detected with full-length hTERT because of reduced levels of hTERT (B). The hTERT truncations were transfected into human 293T cells, immunoprecipitated with anti-flag antibody, and analyzed for telomerase activity by the TRAP assay (D), and hTERT protein levels by Western analysis (E).