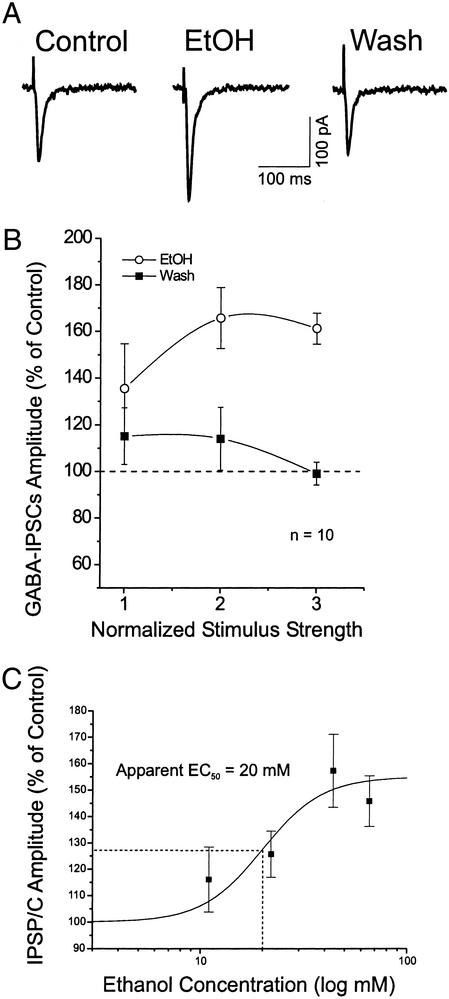
Figure 1.
Acute superfusion of ethanol increases the amplitude of evoked GABA IPSCs, revealed in the presence of glutamatergic blockers. (A) Superfusion of 44 mM ethanol (EtOH) for 10 min increased the IPSC amplitude, with recovery on washout (12 min). (B) Mean percent increases of IPSC amplitudes elicited by 44 mM ethanol, averaged from 10 CeA neurons. (C) Dose–response relationship for ethanol enhancement of mean IPSP/C amplitudes in CeA neurons, expressed as percent of control. Ethanol superfused for 7–10 min. Number of neurons for each ethanol concentration: 11 mM, n = 5; 22 mM, n = 5; 44 mM, n = 8; and 66 mM, n = 4. The logistic curve, plotted by ORIGIN software (Microcal Software, Northampton, MA) using y = (A1 − A2)/[1 + (x/xo)p + A2], gives an apparent EC50 of 20 mM ethanol for IPSP/C enhancement. Parameters of the logistic curve were set at 155% (upper asymptote fixed) and 100% (lower asymptote fixed). The rate was fixed at 3.0, with “center” unfixed. Error bars, SEM.