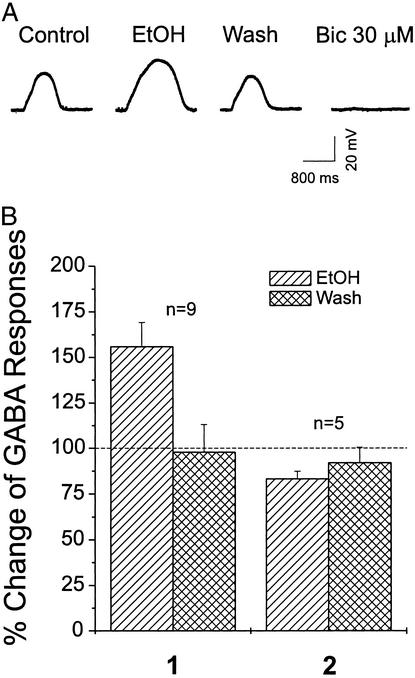
Figure 5.
Amplitudes of exogenous GABA-induced depolarizing potentials in current-clamped CeA neurons are enhanced by 44 mM ethanol (EtOH) superfusion. (A) Representative potential records from a CeA neuron. Local application of GABA (5 μM) from a pipette (every 2 min) during superfusion of ACSF containing APV, CNQX, CGP 55845A, and TTX (control); during ethanol (44 mM) application plus blockers; then during washout of ethanol. Bicuculline (Bic, 30 μM) superfusion totally blocks the GABA response. 1, pooled data from nine ethanol-sensitive CeA neurons showing that ethanol superfusion increased the mean amplitude of exogenous GABA-induced responses, with recovery on washout; 2, in the remaining five cells, 44 mM ethanol slightly decreased mean GABA responses by 17%. The mean ± SEM of GABA responses is plotted as the percent change over the baseline level (dotted line).