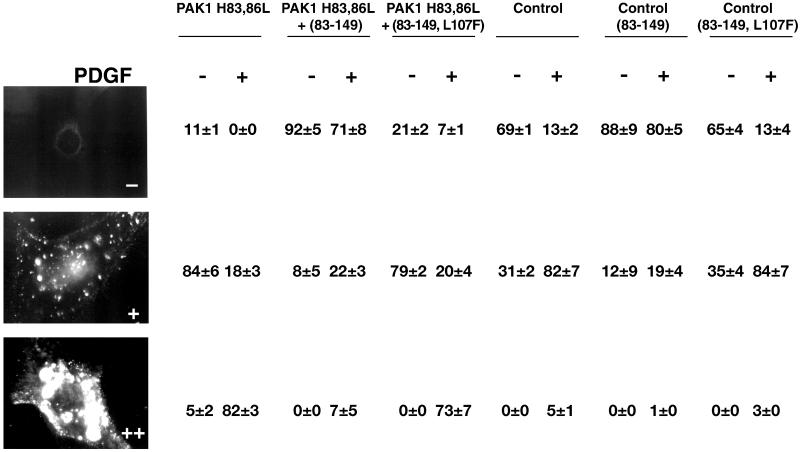
Table 1.
Inhibition of fDx uptake induced by PDGF- and PAK1 (H83,86L) by the PAK1 AID
Serum-starved NIH3T3 cells in which PAK1 (H83,86L) expression was induced by tetracycline withdrawal or repressed by tetracycline maintenance (Control) were infected with Semliki Forest virus containing myc-tagged PAK1 autoinhibitory domain (aa 83–149) or inactivated PAK1 AID (aa 83–149, L107F), as in Edwards et al. (1999). Cells were then either treated without (−) or with (+) 6 ng/ml PDGF, followed by the addition of 0.5 mg/ml lysine-fixable 70-kDa fDx, for 30 min as in MATERIALS AND METHODS. Virally transfected cells were detected by staining with an anti-myc 9E10 antibody followed by a FITC-tagged secondary antibody. Cells were quantitated in a fluorescence microscope using a 40X objective, and scored as −, +, or ++ according to the relative level of fDx uptake, as in the representative fluorescent micrographs shown. A total of 100–216 cells (only myc-staining cells were counted for each condition after viral transfections) were counted per experimental condition in 10 separate fields per coverslip. The values shown are given as a percentage of cells in each scoring category and were calculated as the mean ± SE by using data from three separate experiments performed in duplicate.