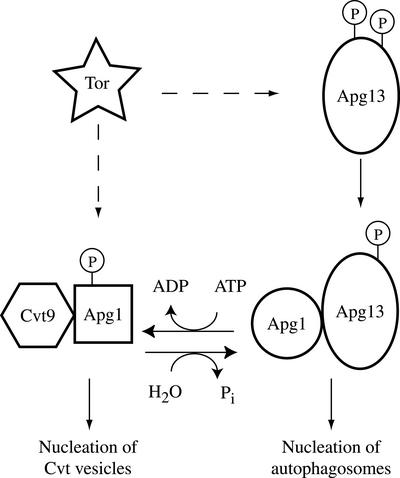
Figure 8.
Model for mechanistic coupling between kinase activity and nucleation of autophagosomes. Under normal growing conditions Tor kinase activity induces Apg1 kinase autophosphorylation, either through modulation of Apg13 phosphorylation or through a direct effect on Apg1. Inhibition of Tor results in a partial dephosphorylation of Apg13, and a decrease of Apg1 kinase autophosphorylation, leading to dephosphorylation and a structural change in Apg1. This structural change is correlated with an increased interaction with Apg13, and involves Cvt9. The dephosphorylated form of Apg1 directs autophagosome formation when associated with Apg13, whereas the phosphorylated form directs nucleation of Cvt vesicles.