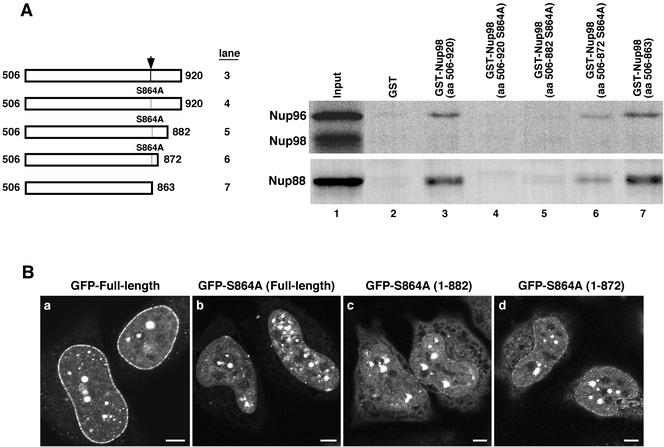
Figure 5.
Nup88 and Nup96 bind to the same domain of Nup98. (A) Truncations were made to the uncleavable GST-Nup98 S864A mutant to remove portions of the C-terminal tail peptide. These truncations were tested in in vitro binding assays with both translated Nup96 and Ha-Nup88. The wild-type and truncated GST fusions bound both translated proteins at the same level (lanes 3 and 7, respectively). The full-length S864A mutant and the 882 truncation mutant did not bind to either Nup96 or Nup88 (lanes 4 and 5). The uncleavable mutant truncated at amino acid 872 bound some Nup88 and Nup96 (lane 6). (B) Truncation mutations were localized as GFP-Nup98 fusions in HeLa cells fixed with 2% paraformaldehyde, 0.2% Triton X-100. The wild-type protein gives the typical strong rim stain observed under these conditions (a), whereas the S864A mutant gives no appreciable rim staining (b). The 882 (c) and 872 (d) truncation mutants give progressively stronger nuclear rim stains. Bar, 5 μm.