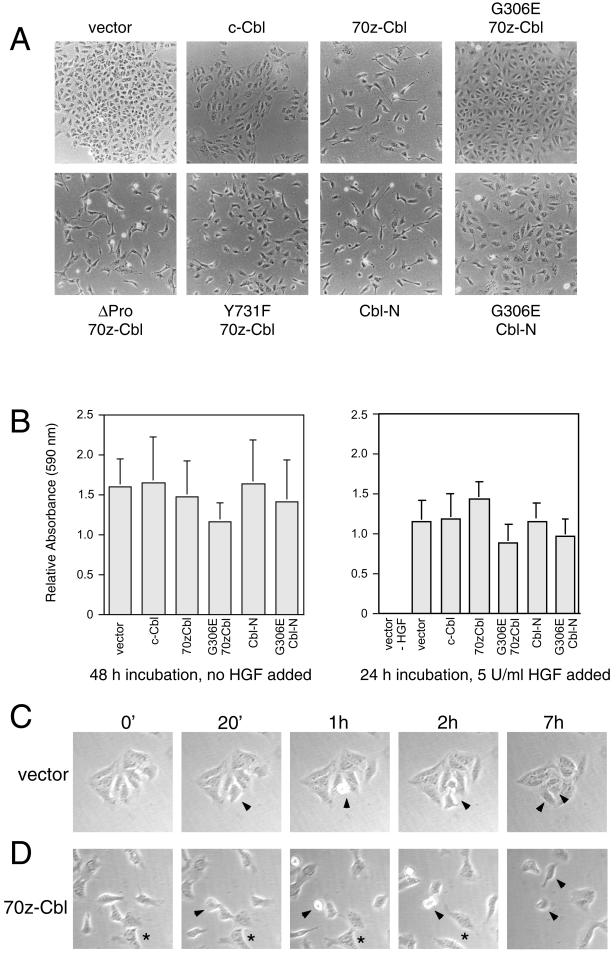
Figure 5.
The SH2/PTB domain of c-Cbl is sufficient to induce morphological changes. (A) MDCK cells were transfected with 70z-Cbl and its variants, as described in MATERIALS AND METHODS, and after selection in hygromycin, changes in cell morphology were visualized by light microscopy. (B) Cells expressing 70z-Cbl and its variants were placed in the upper chamber of a modified Boyden chamber (Neuroprobe; 8 mm, 6 μm) and allowed to migrate through the filter for either 48 h in the absence of HGF stimulation (left panel) or 24 h in the presence of 5 U/ml HGF (right panel). Cells that had traversed the filter were stained with crystal violet, solubilized in 10% acetic acid, and measured at an optical density of 590 nm. Each of these samples was carried out in triplicate. A value of 1 represents the relative motility rate of parental MDCK cells in this assay. MDCK cells (C) and the 70z-Cbl cell line (clone 20) (D) were seeded at low density, and after the formation of small colonies, were subject to time-lapse video microscopy. Photographs were taken of the same field every 20 min for 14 h. The arrowheads in the MDCK (C) and 70z-Cbl (D) panels indicate dividing cells, whereas the asterisks in the images of 70z-Cbl–expressing cells indicate two cells that have dissociated and dispersed.