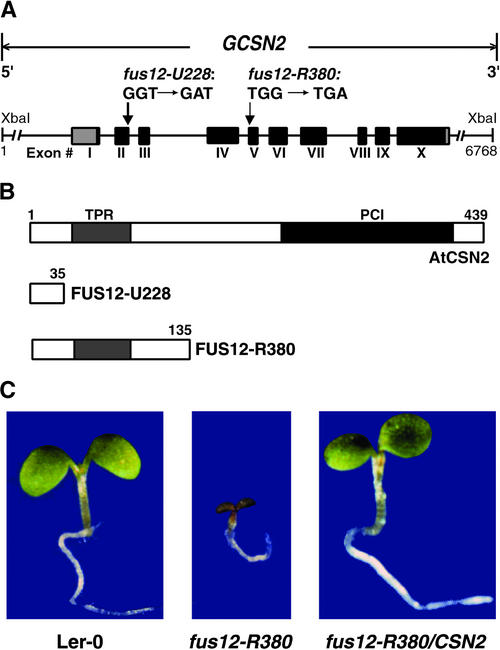
Figure 2.
The FUS12 Locus from Arabidopsis Corresponds to the Gene That Encodes AtCSN2.
(A) Genomic structure of the AtCSN2 locus and molecular nature of the mutations found in the fus12-U228 and fus12-R380 alleles. Introns are shown as lines; boxes and Roman numerals indicate exons. The 5′ and 3′ untranslated regions are shown by gray boxes, and the protein-encoding region is denoted by black boxes. A genomic fragment containing the complete genomic sequence of AtCSN2 together with its own promoter is indicated at top (GCSN2) and was used for the genetic complementation experiment. The two inserts are the mutated sequences found in fus12-R380 and fus12-U228. Numbers indicate base pairs
(B) Wild-type and mutant versions of AtCSN2 proteins. The light gray boxes indicate the TPR homology region; the dark gray box indicates the location of the PCI domain. Numbers indicate amino acid positions.
(C) Seedling phenotype of Landsberg wild type (Ler-0), fus12R380, and fus12-R380/CSN2, a representative line obtained by transforming the fus12-R380 mutant with GCSN2, indicating complementation of the mutant phenotype. All seedlings were grown in the light for 5 days.