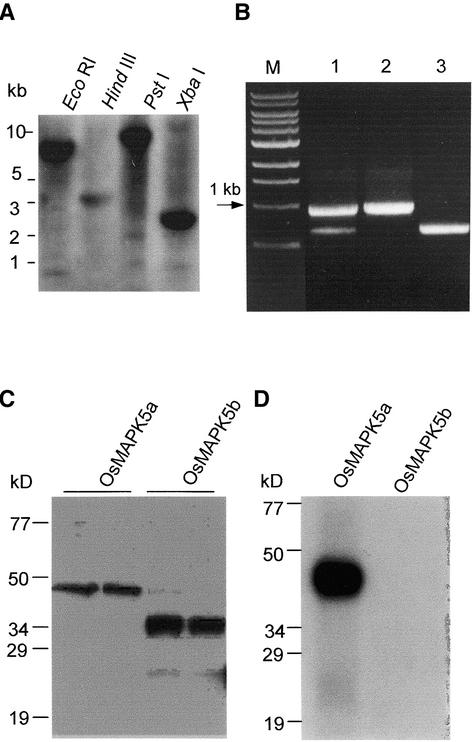
Figure 2.
Genomic Organization, Alternative Splicing, Recombinant Proteins, and Autophosphorylation Activity of OsMAPK5.
(A) DNA gel blot analysis of the OsMAPK5 gene. Total DNA from cv Drew (4 μg for each lane) was digested individually with EcoRI, HindIII, PstI, and XbaI and hybridized with a gene-specific probe covering the region from nucleotide 999 to the 3′ end of the OsMAPK5a cDNA.
(B) RT-PCR analysis using a primer pair covering the differentiated regions of the OsMAPK5a and OsMAPK5b cDNAs. The blast fungus–induced (2 days after infection) mRNAs from cv Drew were used for RT-PCR analysis (lane 1). The cDNAs of OsMAPK5a and OsMAPK5b also were used for PCR with the same primer pair (lanes 2 and 3). M, DNA size markers.
(C) In vitro expression of OsMAPK5a and OsMAPK5b, and specificity of the OsMAPK5 antibody. One hundred nanograms of total protein from E. coli (left lanes) or 10 ng of affinity-purified fusion protein of His-OsMAPK5a and His-OsMAPK5b (right lanes) was separated by 10% SDS-PAGE and detected with the anti-OsMAPK5 antibody.
(D) In vitro autophosphorylation assay of the affinity-purified fusion proteins His-OsMAPK5a and His-OsMAPK5b.