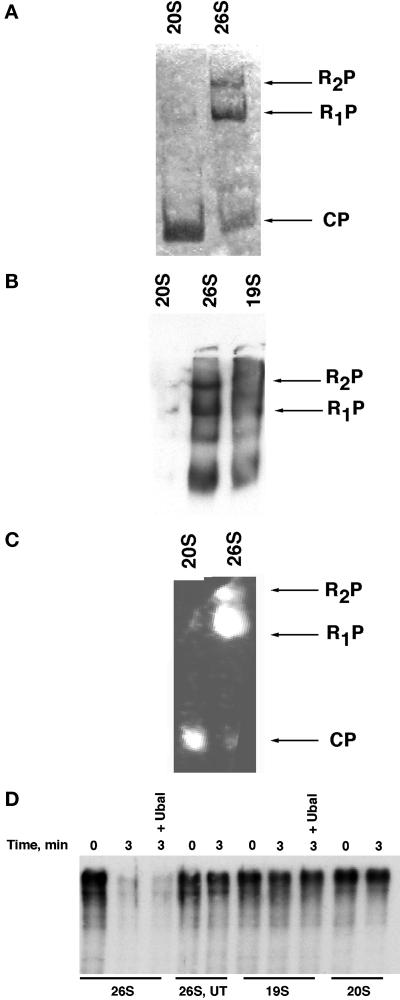
Figure 2.
Functional analysis of affinity-purified 26S proteasomes, plus 19S and 20S subcomplexes (A and B) 26S, 19S, and 20S preparations were electrophoresed on nondenaturing polyacrylamide gels and analyzed by Coomassie blue staining directly (A), or transferred to nitrocellulose and immunoblotted with anti-Rpt1 serum (B). CP refers to the 20S core particle, whereas R1P and R2P refer to core particles decorated with either one or two regulatory caps, respectively. Note that no 20S could be detected by Ponceau S staining after transfer to nitrocellulose membranes. (C) Peptidase activity of proteasomal preparations toward the fluorogenic peptide N-succinyl-Leu-Leu-val-Tyr 7-amido-4-methylcoumarin was evaluated by incubating a native gel containing fractionated samples for 10 min at 30°C in the presence of 100 μM substrate and 1 mM ATP. The fluorescent bands were visualized by exposure to UV light (360 nm). (D) Trimeric complex of Sic1/Cdc28/Clb5 purified from insect cells was phosphorylated by immobilized G1 Cdk complexes and subsequently ubiquitinated by immobilized tetrameric SCFCdc4 ubiquitin ligase in the presence of E1, E2 (Cdc34), ATP, and ubiquitin (Seol et al., 1999). The soluble fraction containing ubiquitinated Sic1 (500 nM) was supplemented with 100 nM 26S, 19S, or 20S complexes and incubated at 30°C for 0–3 min in the presence of an ATP-regenerating system. Reactions were terminated by the addition of SDS Laemmli buffer, resolved by SDS-PAGE, and evaluated by immunoblotting with anti-Sic1 polyclonal antibodies. UT refers to Flag eluate from an untagged strain; reactions marked + Ubal contained 2 μM ubiquitin aldehyde (Calbiochem, La Jolla, CA).