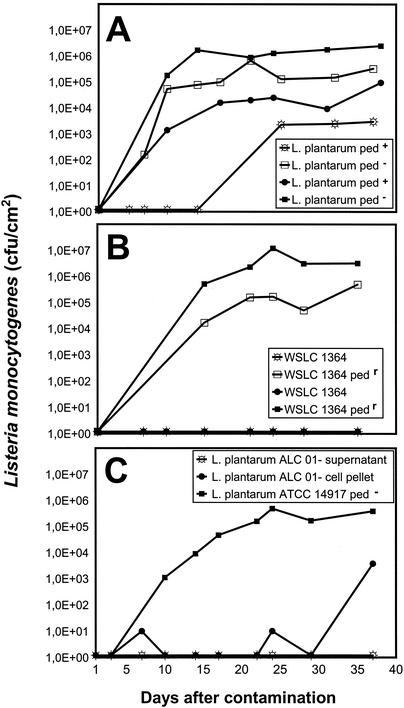
FIG. 1.
Inhibition of growth of L. monocytogenes WSLC 1364 by L. plantarum ALC 01. Ripening experiments were performed on soft cheese using a commercial, undefined multispecies microbial consortium. (A) Listeria cell counts on the cheese surface after contamination at day 1 with 2 × 102 CFU (open symbols) and 4 × 103 CFU (solid symbols) per ml of brine solution. Control cheeses were ripened with the pediocin AcH-negative type strain L. plantarum ATCC 14917. (B) Contamination with 102 CFU (open symbols) or 103 CFU (solid symbols) per ml of brine solution. Control cheeses were contaminated with the resistant mutant WSLC 1364R (pedr). (C) Listeria contamination with 7 × 102 CFU/ml of brine solution. In this case, cheese ripening was performed with a commercial, defined ripening culture. Either the supernatant or the pellet of the 14-h culture in VisStart TW ALC01 medium was used. Control cheeses were ripened with the addition of a 14-h culture of the pediocin AcH-negative type strain L. plantarum ATCC 14917, cultivated in VisStart TW ALC01.