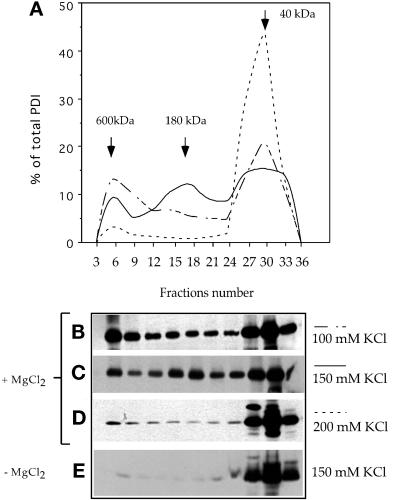
Figure 7.
PDI forms several salt-dependent complexes. A crude membrane fraction from wild-type AX2 cells was subjected to Triton X-114 phase partitioning in the presence or absence of MgCl2 and 100, 150, or 200 mM KCl. The aqueous phase was loaded onto a Superdex 200 HR 10/30 gel filtration column. The fractions were electrophoresed on 12% SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions and immunoblotted with anti-PDI antibodies. (A) Elution profiles showing progressive disruption of the high-molecular-mass complexes by increasing KCl concentrations. Representative immunoblots of elution profiles performed in 100 mM KCl (B), 150 mM KCl (C), and 200 mM KCl (D). At 150 mM salt, three forms were present at 600, 180, and 40 kDa, but at 200 mM, only the monomeric form of 40 kDa was visible. (E) Extraction and elution were performed with 150 mM KCl but in the absence of MgCl2. Under these conditions, PDI was found almost exclusively as a monomer. Molecular mass standards: thyroglobulin, 680 kDa; ferritin, 420 kDa; catalase, 205 kDa; and aldolase, 165 kDa. Densitometric quantifications were performed with NIH Image 1.61. The amount of PDI and GFP in each fraction is represented as the percentage of total eluted protein.