Figure 1.
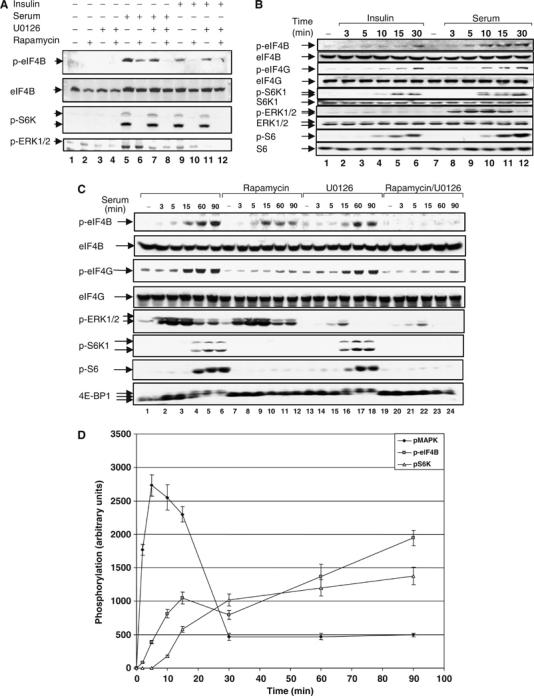
Rapamycin-resistant eIF4B Ser422 phosphorylation is mediated by ERK1/2 MAPK signaling. (A) HeLa cells were deprived of serum in the presence or absence of 20 nM rapamycin for 16–18 h. Cells were pretreated with 10 μM of U0126 for 2 h, and then stimulated with either 20% serum or insulin (100 nM) for 30 min. Total cell extracts were subjected to SDS–PAGE followed by immunoblotting with phospho-eIF4B S422, phospho-S6K1 T389, and phospho-ERK1/2 T202/Y204 antibodies and the membrane was reprobed with anti-eIF4B antiserum. (B) HeLa cells were starved for serum as in (A) and stimulated for the indicated times with either 20% serum or insulin (100 nM). Cell extracts were resolved by SDS–PAGE and immunoblotted with phospho-eIF4G S1108, phospho-eIF4B S422, phospho-S6K1 T389, phospho-ERK1/2 T202/Y204, phospho-S6 S240/244 antibodies and the indicated total proteins. (C) HeLa cells were deprived of serum in the presence or absence of 20 nM rapamycin for 16–18 h. Cells were pretreated with 10 μM of U0126 for 2 h, and then stimulated with 20% serum for the indicated times. Total cell extracts were resolved by SDS–PAGE, immunoblotted with phospho-eIF4G S1108, phospho-eIF4B S422, phospho-S6K1 T389, phospho-ERK1/2 T202/Y204, and phospho-S6 S240/244 antibodies and reprobed for the indicated proteins with pan-specific antibodies. (D) Sequential activation of signaling pathways involved in eIF4B Ser422 phosphorylation. HeLa cells were deprived of serum for 16–18 h. Cells were then stimulated with 20% serum for the indicated amounts of time. Protein extracts were resolved by SDS–PAGE and probed for phospho-eIF4B S422, phospho-ERK1/2 T202/Y204, and phospho-S6K T389.
